Curiosity Navigation Curiosity Home Mission Overview Where is Curiosity? Mission Updates Science Overview Instruments Highlights Exploration Goals News and Features Multimedia Curiosity Raw Images Images Videos Audio Mosaics More Resources Mars Missions Mars Sample Return Mars Perseverance Rover Mars Curiosity Rover MAVEN Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Mars Odyssey More Mars Missions Mars Home 3 min read
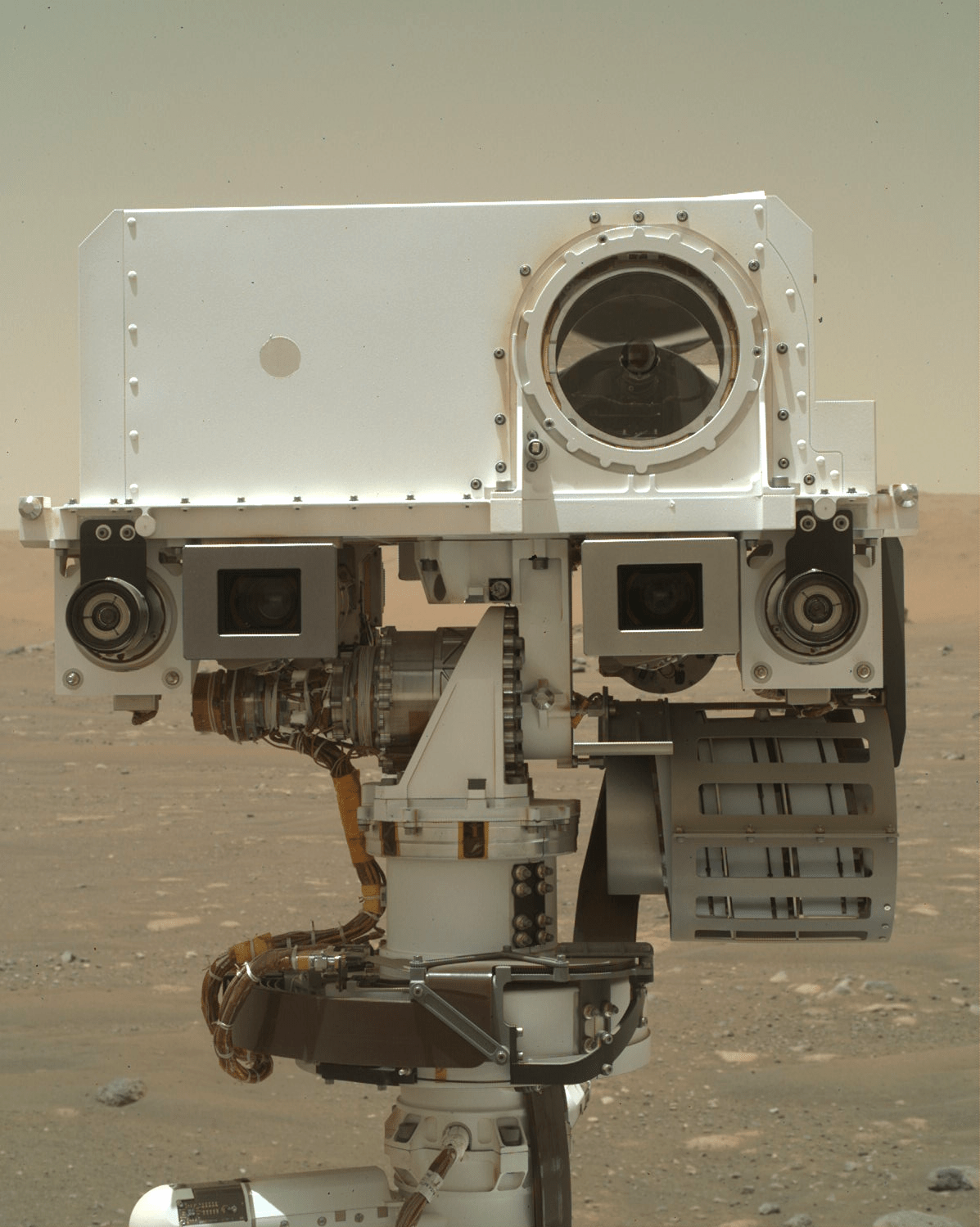
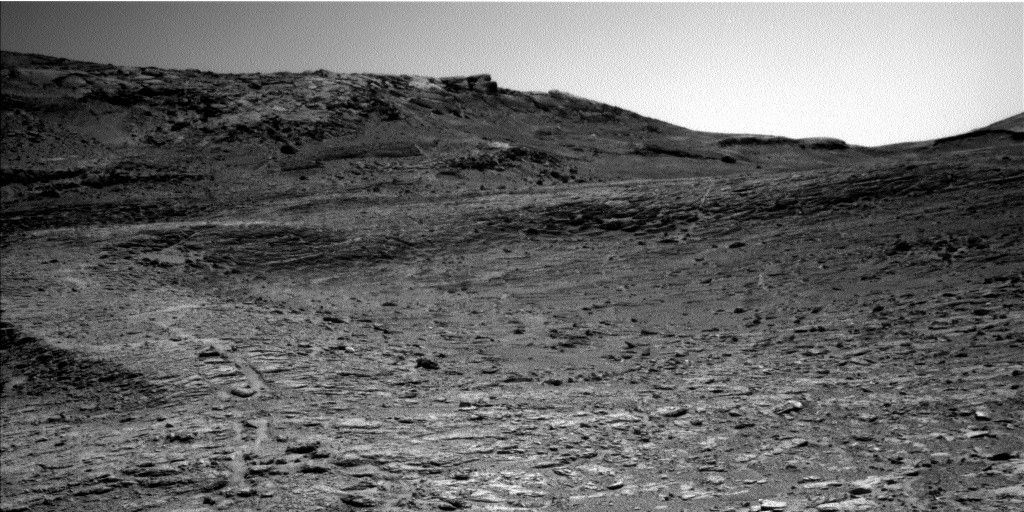
Curiosity Blog, Sols 4634-4635: A Waiting Game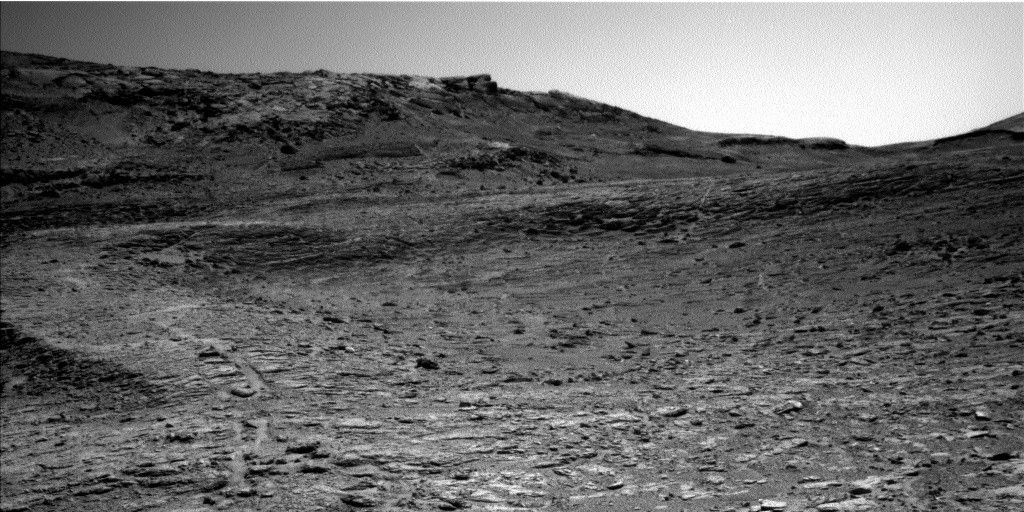  NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity acquired this image using its Left Navigation Camera on Aug. 18, 2025 — Sol 4633, or Martian day 4,633 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission — at 12:39:47 UTC. NASA/JPL-Caltech Written by Lucy Thompson, Planetary Scientist and APXS Team Member, University of New Brunswick, Canada
NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity acquired this image using its Left Navigation Camera on Aug. 18, 2025 — Sol 4633, or Martian day 4,633 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission — at 12:39:47 UTC. NASA/JPL-Caltech Written by Lucy Thompson, Planetary Scientist and APXS Team Member, University of New Brunswick, Canada
Earth Planning Date: Monday, Aug. 18, 2025
The downlink data from our weekend activities arrived on Earth as we started planning this morning. As the APXS payload uplink and downlink lead, I assess the downlink data to ensure that our observations executed and that the instrument is healthy before we can proceed with the day’s activities. We also need that downlink data to assess which targets we can safely touch with Curiosity’s arm, to place APXS and MAHLI to analyze chemistry and closeup textures, respectively, as well as target for Mastcam and ChemCam, and plan the next drive. Because of the relatively late downlink, we all waited patiently for the necessary data to be processed before we could really start to plan in earnest.
It is always exciting to see our new parking spot and the view in front of the rover. Today was no exception. The drive executed as planned and we are on stable ground, which will enable us to unstow the arm for contact science with APXS and MAHLI.
We selected a representative bedrock patch (“Gil”) that was large enough and smooth enough to brush for dust removal, and to place APXS and MAHLI on. ChemCam will also analyze this target with LIBS, and Mastcam will capture a documentation image. The bedrock at this location is representative of an intermediate zone between the large resistant ridges and hollows that comprise the boxwork terrain that we are currently exploring. Mastcam will image the wall of a prominent resistant ridge that we are driving to (“Río Frío”), as well as a narrow, sand-filled trough (“Cusi Cusi”). The remote long-distance imaging capabilities of ChemCam will be used to look at the base of the Mishe Mokwa butte, off to the east.
Observations to monitor the atmosphere are also planned before we drive away from this location. They include a Navcam large dust-devil survey and suprahorizon movie, and a Mastcam tau observation to observe dust in the atmosphere. After the touch (and targeted science) part of this touch-and-go plan, the drive (go part) should take us about 36 meters (about 118 feet) to the wall of Río Frío. (see associated image).
After the drive, we will document the ground beneath the rover’s wheels with MARDI before some untargeted science. Mastcam will again image Río Frío in early morning light, trying to highlight structures and veins that might be present, and ChemCam will utilize their autonomous targeting capabilities to analyze a bedrock target in our new workspace. Two more atmospheric observations are also squeezed in before we hand over to the next plan: a Navcam cloud-altitude observation and line-of-sight scan.
Standard REMS, DAN and RAD activities round out this jam-packed plan. The downlink was well worth the wait!
Want to read more posts from the Curiosity team?
Visit Mission Updates
Want to learn more about Curiosity’s science instruments?
Visit the Science Instruments page
 NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity at the base of Mount Sharp NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity at the base of Mount Sharp NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
Details Last Updated Aug 19, 2025 Related Terms Blogs
Keep Exploring Discover More Topics From NASA Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun, and the seventh largest. It’s the only planet we know of inhabited…

Explore this collection of Mars images, videos, resources, PDFs, and toolkits. Discover valuable content designed to inform, educate, and inspire,…

Each robotic explorer sent to the Red Planet has its own unique capabilities driven by science. Many attributes of a…
Mars Exploration: Science Goals
The key to understanding the past, present or future potential for life on Mars can be found in NASA’s four…


 2 min read Curiosity Blog, Sols 4631-4633: Radiant Ridge Revolution
2 min read Curiosity Blog, Sols 4631-4633: Radiant Ridge Revolution
 2 min read Curiosity Blog, Sols 4629-4630: Feeling Hollow
2 min read Curiosity Blog, Sols 4629-4630: Feeling Hollow
 2 min read Curiosity Blog, Sols 4627-4628: A Ridge Stop in the Boxworks
2 min read Curiosity Blog, Sols 4627-4628: A Ridge Stop in the Boxworks
