Curiosity Navigation Curiosity Home Mission Overview Where is Curiosity? Mission Updates Science Overview Instruments Highlights Exploration Goals News and Features Multimedia Curiosity Raw Images Images Videos Audio Mosaics More Resources Mars Missions Mars Sample Return Mars Perseverance Rover Mars Curiosity Rover MAVEN Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Mars Odyssey More Mars Missions Mars Home 2 min read
Sols 4481-4483: Humber Pie 
Earth planning date: Friday, March 14, 2025
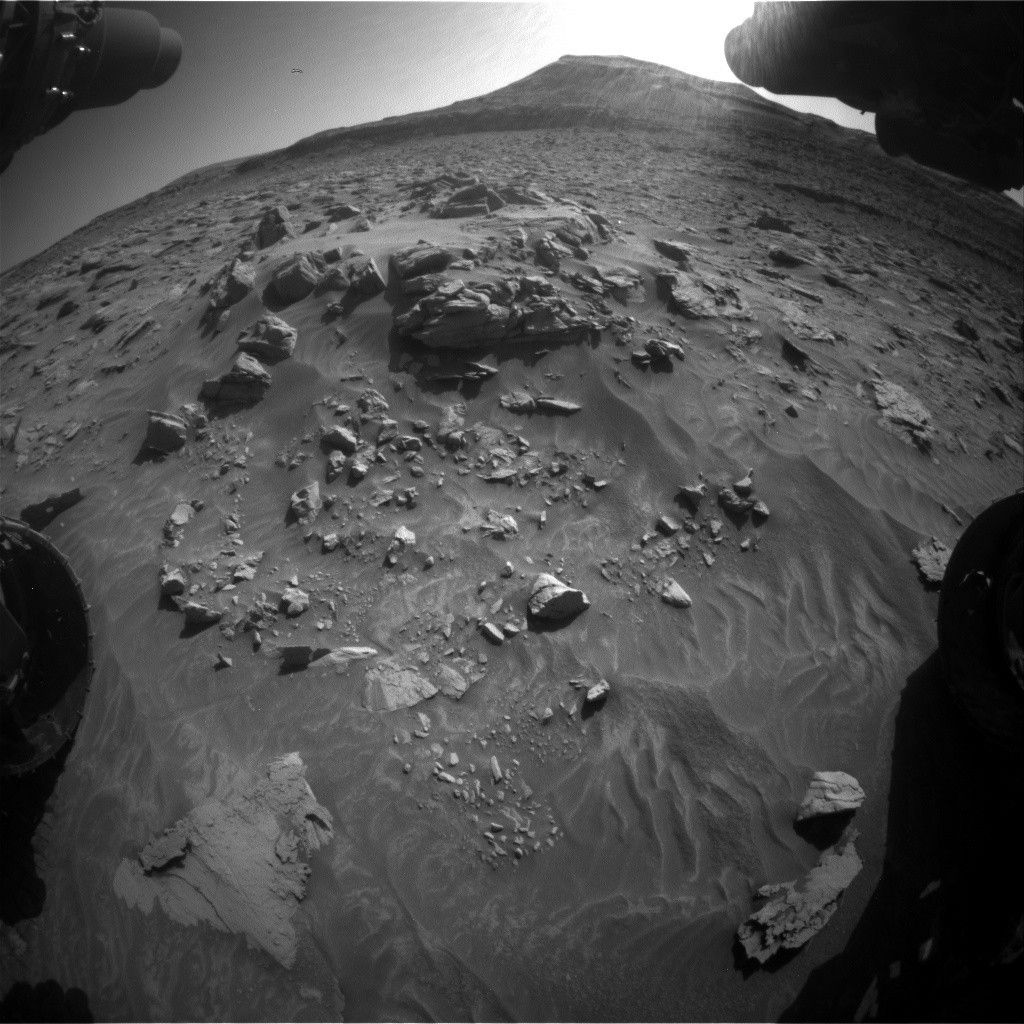
The rover successfully arrived at the “Humber Park” outcrop which, on this fine “Pi Day” on Earth, we could convince ourselves looked like a pie with a sandy interior and a rough and rocky crust. We can only hope our instruments are as excited to tuck into this outcrop as the Curiosity team is to eat our pizzas and favorite pies (for me, pumpkin) this afternoon and evening.
MAHLI gets a big serving of rock structures from the Humber Park “crust” with three separate imaging targets. One observation, at the target “Yerba Buena Ridge,” covers structures expressed across the front of the outcrop in the above image. A second target, “Sepulveda Pass,” has intriguing texture that warranted multiple flavors of stereo imaging. The final target, which MAHLI shared with APXS, was “South Fork.” It was the clearest place to put APXS down on the rough bedrock blocks.
ChemCam also feasted on rock chemistry from an array of targets with different textures. “Ridge Route” covered a low-lying bedrock slab with the fine layering we have seen consistently through the sulfate unit, while “Toyon Canyon” covered a lumpier portion of the Humber Park outcrop above Yerba Buena Ridge. The “Mount Lawlor” target was a mix of Ridge Route and Toyon Canyon — layered, but on a high-standing portion of the outcrop that also had some unusual chains of pits. ChemCam added two long distance mosaics on “Gould Mesa” to the menu, which captured a variety of structures on this impressive butte about 100 meters ahead of the rover.
Mastcam focused on covering the whole of Humber Park with a stereo mosaic but also added small mosaics across a trough in the sand and a bedrock block with potential cross bedding at “Rancho Los Feliz.” Because just imaging this side of Humber Park was not enough, Mastcam and Navcam worked closely with the rover drivers to plan a mid-drive mosaic of the other side of the outcrop so we fully capture Humber Park’s “crust.”
Our environmental observations were not just pie in the sky but will help us monitor the chemistry of and the amount of dust in the atmosphere, and record clouds and dust devils crossing above and around us.
Details Last Updated Mar 18, 2025 Related Terms Blogs
Keep Exploring Discover More Topics From NASA Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun, and the seventh largest. It’s the only planet we know of inhabited…

Explore this collection of Mars images, videos, resources, PDFs, and toolkits. Discover valuable content designed to inform, educate, and inspire,…

Each robotic explorer sent to the Red Planet has its own unique capabilities driven by science. Many attributes of a…
Mars Exploration: Science Goals
The key to understanding the past, present or future potential for life on Mars can be found in NASA’s four…
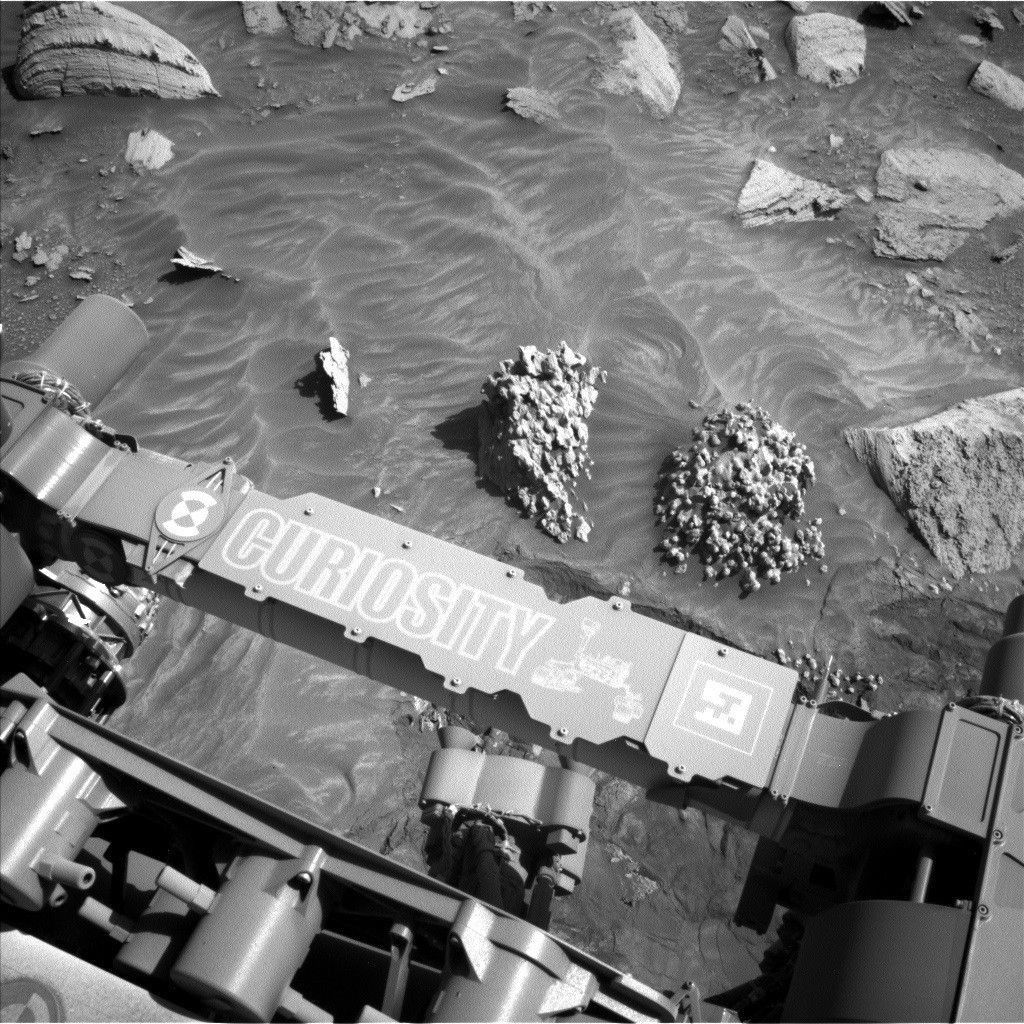


 3 min read Sols 4479-4480: What IS That Lumpy, Bumpy Rock?
3 min read Sols 4479-4480: What IS That Lumpy, Bumpy Rock?
 3 min read Navigating a Slanted River
3 min read Navigating a Slanted River
 2 min read Sols 4477-4478: Bumping Back to Business
2 min read Sols 4477-4478: Bumping Back to Business
