Explore This Section Earth Earth Observer Editor’s Corner Feature Articles Meeting Summaries News Science in the News Calendars In Memoriam Announcements More Archives Conference Schedules Style Guide  7 min read
7 min read
Sentinel-6B Extends Global Ocean Height Record Introduction
On November 16, 2025, the Sentinel-6B satellite launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California. The mission is a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and several European partners – the European Space Agency (ESA), the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), the French Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), and the European Commission. Its objective is to continue collecting data to extend the ocean height record, which was started in 1992 with the U.S./French TOPEX/Poseidon satellite mission. During the past three decades, NASA and its partners have operated a satellite in the same orbit, precisely tracking the height of the oceans across the globe, once every 10 days.
Sentinel-6B took to the skies almost five years to the day after its twin, Sentinel-6A, which launched November 20, 2020, also from VSFB, and was renamed Sentinel–6 Michael Freilich, honoring the former head of NASA’s Earth Science Division – see The Editor’s Corner [March–April 2020, 32:1, 1–2]. Together, the two missions comprise the international Sentinel-6/Jason – Continuity of Service (CS) mission, which will provide continuity with past missions from TOPEX/Poseidon through Jason-3. Sentinel-6B will continue to measure sea level to about one inch (2.5 cm), extend the record of atmospheric temperatures, and continue sea level observations through the end of the 2020s.
The article that follows briefly introduces Sentinel-6B’s payload (which is the same as Sentinel–6 Michael Freilich). It then describes the planned science applications of the mission, followed by a brief conclusion.
Sentinel-6B Payload
The Sentinel-6B satellite carries several instruments to support the mission’s science goals – see Figure 1. A Radar Altimeter bounces signals off the ocean surface to determine the distance to the ocean. An Advanced Microwave Radiometer (AMR) retrieves the amount of water vapor between the satellite and ocean, which affects the travel speed of radar pulses, providing a critical correction to the distance measured by the radar. Other onboard instruments are used to precisely determine the satellite’s position [e.g., Doppler Orbitography by Radiopositioning Integrated on Satellite (DORIS) and Laser Retroreflector Array]. The height of the ocean surface can be calculated by combining the satellite’s position with the distance to the ocean. In addition, S- and X-band antennas perform data downlinks, and a solar array supplies power.
Beyond these instruments, Sentinel-6B contains Global Navigation Satellite System Radio Occultation (GNSS-RO) instrument that will aid with weather prediction. Observations made between the spacecraft instrument and other GNSS satellites as they disappear over Earth’s limb, or horizon, will provide detailed information about variations in the layers of the atmosphere. This information will contribute to computer models that predict the weather and enhance forecasting capabilities.
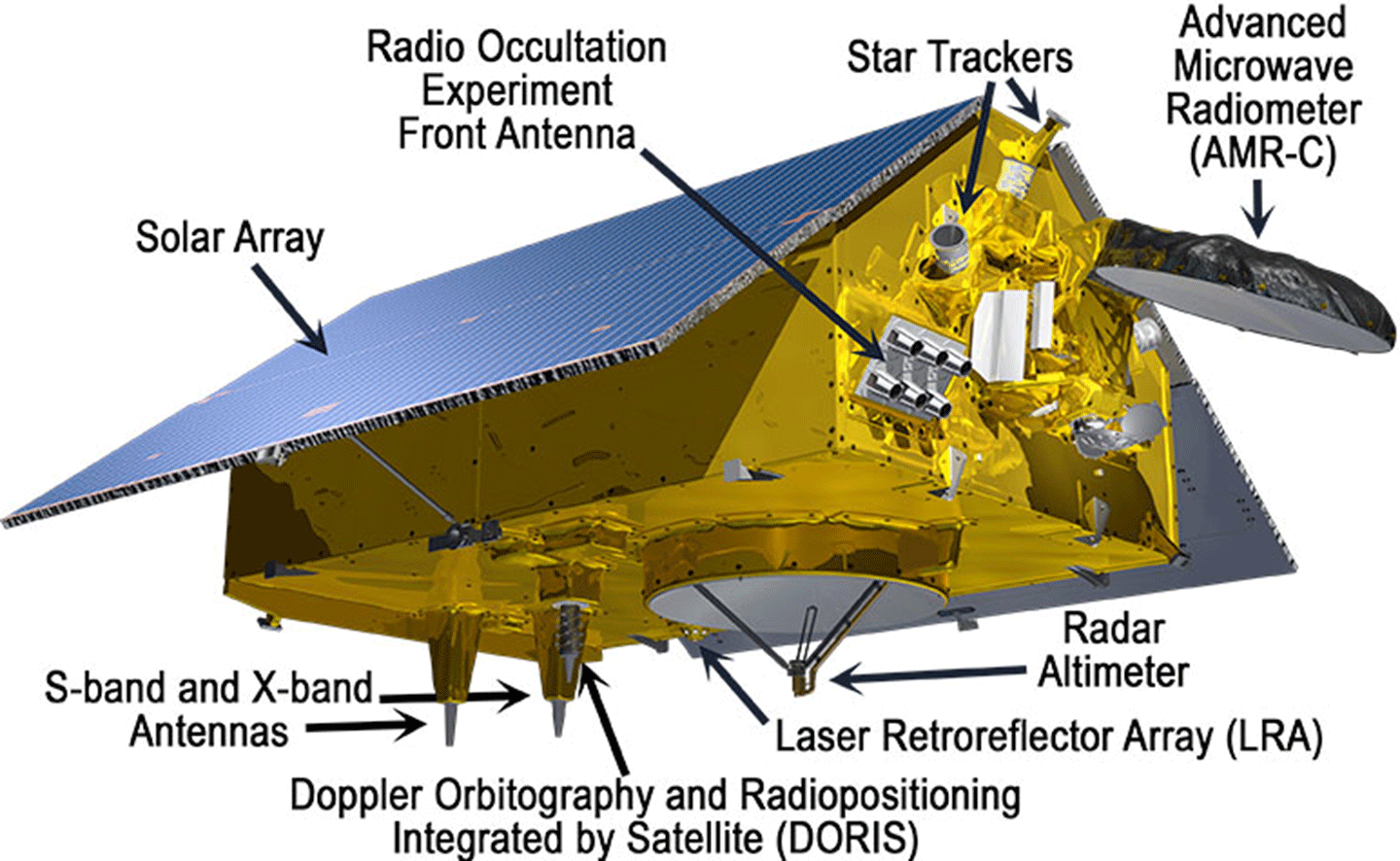 Figure 1. Sentinel-6B contains an array of instruments to continue to measure ocean height and gather other integral information about the global ocean. Figure credit: NASA/JPL Sentinel-6B Science
Figure 1. Sentinel-6B contains an array of instruments to continue to measure ocean height and gather other integral information about the global ocean. Figure credit: NASA/JPL Sentinel-6B Science
The subsections that follow give a short preview of Sentinel-6B’s science capabilities, which are identical to those of Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich and similar – albeit enhanced – to the capabilities of previous satellite altimetry missions.
Measuring Ocean Height
Ocean height is a critical measurement because it provides a host of information about the movement of surface currents, transfer of energy around the planet, and an early warning system for large-scale climate phenomena, like El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) – see further discussion of ENSO below. Satellites obtain this data using altimeters, which send a radar pulse to the ocean surface every second and measure the time it takes to return. Pairing these data with the satellite’s precise location provides a measure of the height of the ocean water with an accuracy of within a few centimeters.
But the simplicity of the measurement belies the volumes of information that can be gleaned from the height of the oceans. As water moves from one place to another, it tilts the surface of the ocean, and by measuring this tilt the sea level satellites allow scientists to calculate ocean currents – see Figure 2.
 Figure 2. Surface current estimates calculated using the Ocean Surface Current Analyses Real-time (OSCAR) global surface current database – which is made based on input from satellites that measure ocean height. Sentinel-6B will be the latest satellite to provide real-time data that are accurate enough for OSCAR to compute these currents. This will allow forecasters to accurately predict ocean currents and marine weather conditions globally, every single day. Figure credit: Severine Fournie [JPL] Tracking the Expansion and Contraction of Water in the Ocean
Figure 2. Surface current estimates calculated using the Ocean Surface Current Analyses Real-time (OSCAR) global surface current database – which is made based on input from satellites that measure ocean height. Sentinel-6B will be the latest satellite to provide real-time data that are accurate enough for OSCAR to compute these currents. This will allow forecasters to accurately predict ocean currents and marine weather conditions globally, every single day. Figure credit: Severine Fournie [JPL] Tracking the Expansion and Contraction of Water in the Ocean
Ocean height data also provide information about ocean water temperature. Since water expands as it warms, a warm patch of ocean measures several inches taller than a cold patch – see Figure 3. Ocean height measurements thus can be used to reveal how the ocean stores and redistributes heat and energy, which are key drivers of Earth’s climate.
By observing ocean heights, Sentinel-6B will help improve forecasters’ ability to predict storm intensity and scientists’ ability to track long-term trends in heat storage. Information on ocean height also outlines ocean currents, eddies, and tides, which helps scientists understand how heat, nutrients, carbon, and energy are transported around Earth. These observations are essential for understanding Earth’s energy balance, ocean circulation, and the role of the ocean in shaping weather and climate patterns.
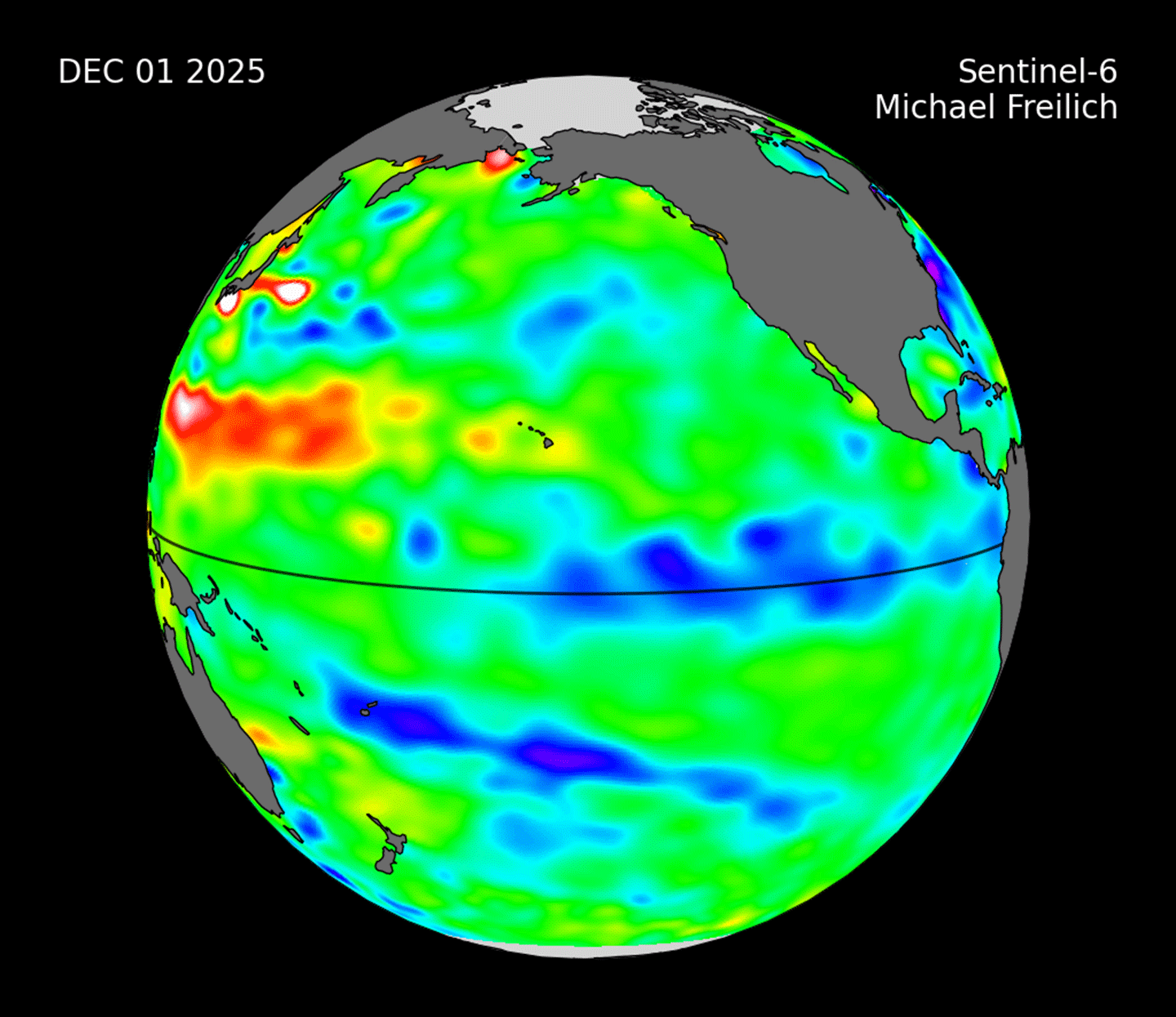 Figure 3. Ocean height data obtained on September 8, 2025, from Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich for the Pacific Ocean, where blue shows lower than normal heights along the equator in the east associated with a mild to moderate La Niña event. Figure credit: NASA Using Ocean Height Measurements to Track ENSO
Figure 3. Ocean height data obtained on September 8, 2025, from Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich for the Pacific Ocean, where blue shows lower than normal heights along the equator in the east associated with a mild to moderate La Niña event. Figure credit: NASA Using Ocean Height Measurements to Track ENSO
The movement of heat within the ocean is linked to weather and climate conditions across the globe. For reasons not completely understood, the waters of the Pacific Ocean experience a periodic fluctuation between warm and cool in the eastern tropical Pacific; this cycle is called ENSO. During an El Niño event in the Pacific Ocean, unusually warm water (which is visible in the satellite data as higher than normal sea levels) builds up along the equator in the east. The pool of warm water shifts rainfall patterns across the United States and Canada. This change is telescoped around the globe, altering normal weather patterns. Conversely, La Niña events develop when cooler waters accumulate along the eastern Pacific (and hence, lower than normal sea levels). In this way, the satellite observations of sea level help scientists and forecasters better see how the ocean is changing and the type of weather conditions to expect in the coming months – see Figure 4.
Higher sea levels usually mean warmer waters, not just at the surface, but over a range of depths. This means that high sea levels can also herald rapidly intensifying storms. Meteorologists can use this information when tracking tropical storms that gain energy from warm patches of ocean water and intensify into hurricanes – often rapidly.
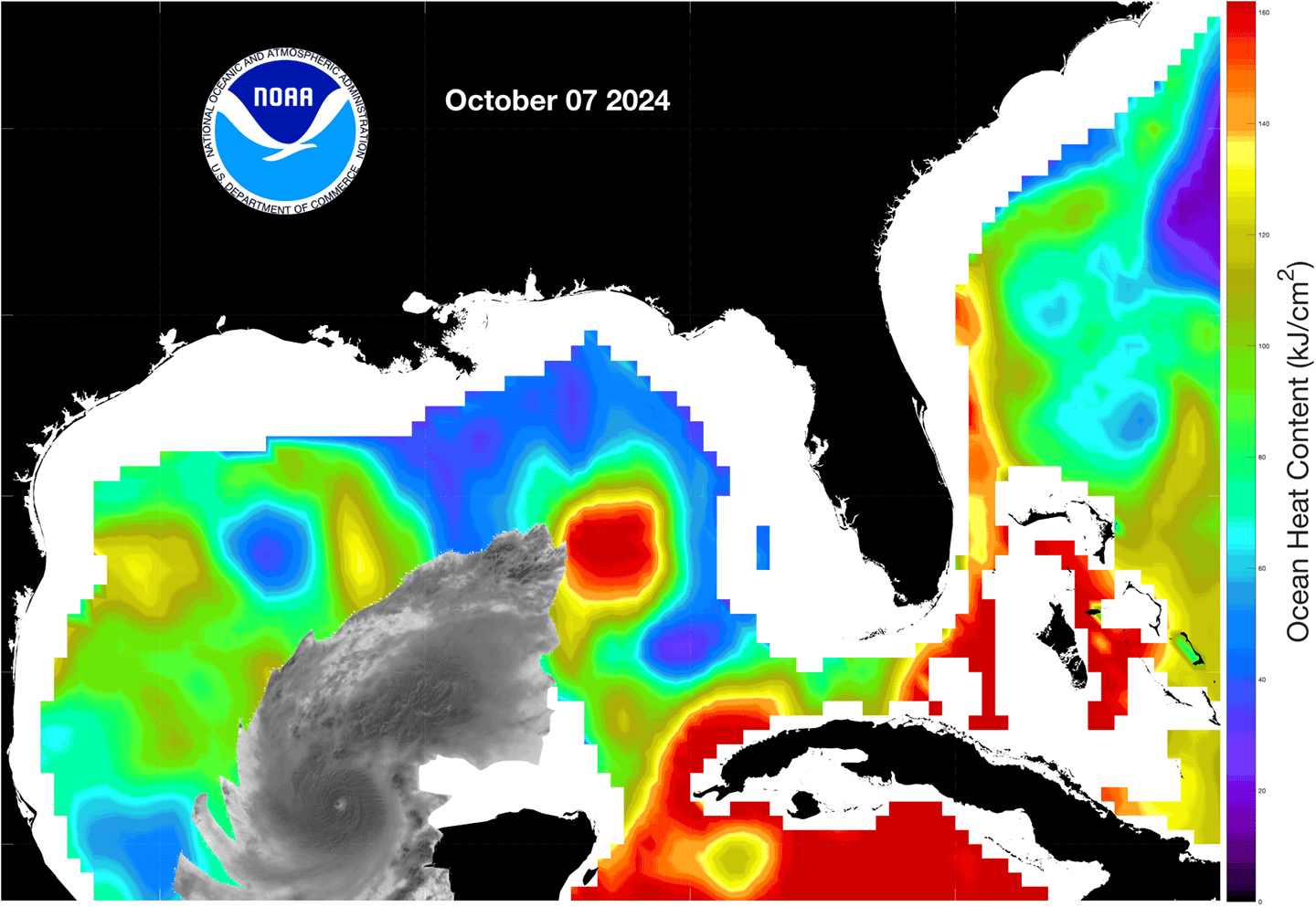
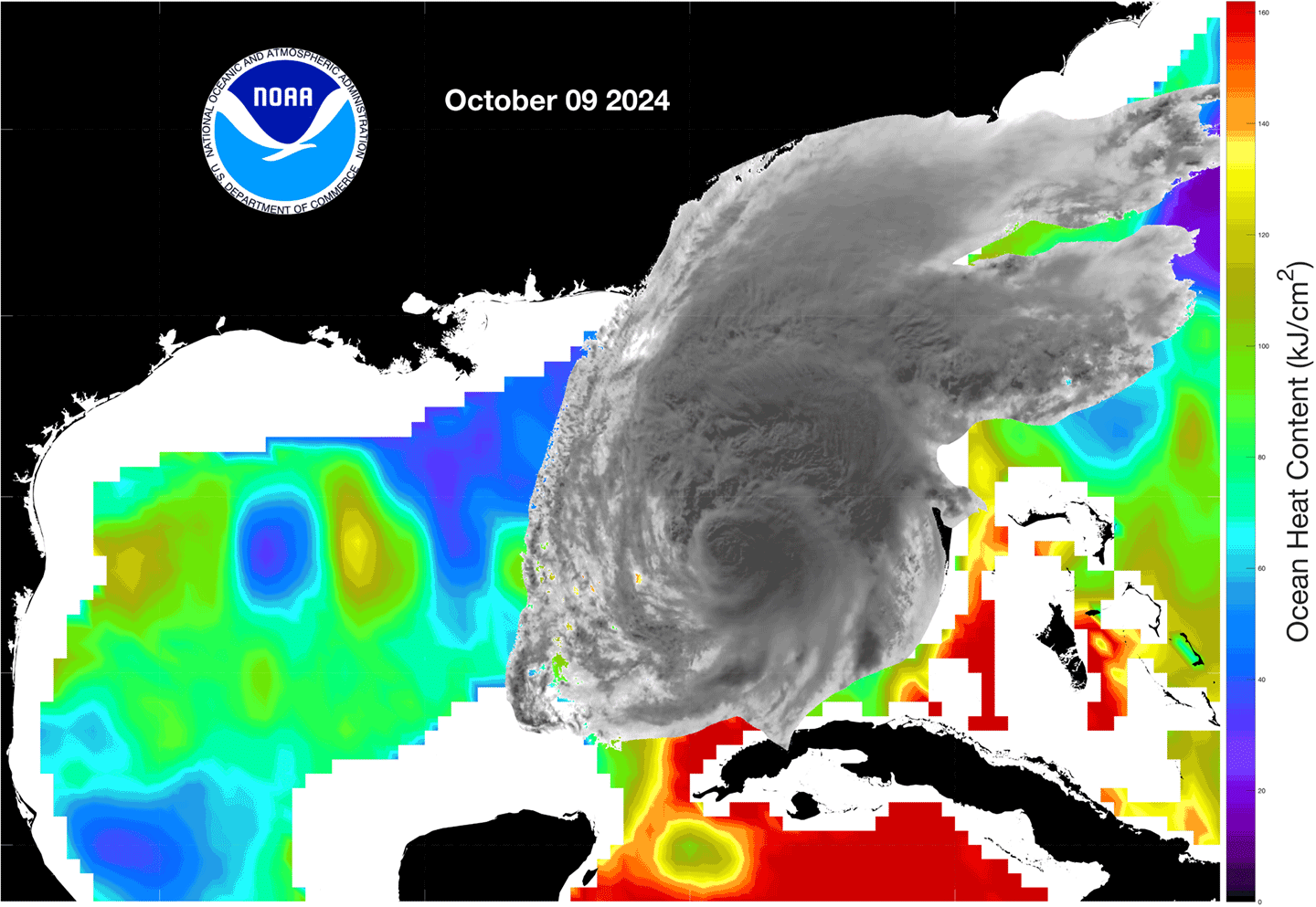 Figure 4. As Hurricane Milton passed over the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico on its approach to Florida in October 2024, the storm experienced a period of rapid intensification. This image pair shows ocean heat estimates based on observations from Jason-CS on October 7, 2024 [top] and October 9, 2024 [bottom]. Red and yellow indicate warmer than normal temperatures, where blue and green represent cooler than normal temperatures. A satellite image of the hurricane is overlaid to indicate the storm’s position as it moved toward Florida’s west coast. Notice that the period of rapid intensification corresponds to the storm moving over the patch of anomalously warm water that can be seen in the center of the image [red]. Figure credit: NOAA Monitoring Ocean Changes
Figure 4. As Hurricane Milton passed over the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico on its approach to Florida in October 2024, the storm experienced a period of rapid intensification. This image pair shows ocean heat estimates based on observations from Jason-CS on October 7, 2024 [top] and October 9, 2024 [bottom]. Red and yellow indicate warmer than normal temperatures, where blue and green represent cooler than normal temperatures. A satellite image of the hurricane is overlaid to indicate the storm’s position as it moved toward Florida’s west coast. Notice that the period of rapid intensification corresponds to the storm moving over the patch of anomalously warm water that can be seen in the center of the image [red]. Figure credit: NOAA Monitoring Ocean Changes
Sentinel-6B can also monitor changes in sea level. Over 90% of the heat trapped by the Earth is stored in the oceans. That heat warms the water, which takes up more space and accounts for about one-third of the observed global rise in sea level. The remainder is driven by melting glaciers and ice sheets, which add water to the oceans as well. The result is a long-term rise in sea level by more than 10 cm (4 in) since the early 1990s, when TOPEX/Poseidon was launched.
A record of global mean sea level change for the past three decades reveals an annual oscillation that reflects the natural movement of water between the ocean and the land, much like the heartbeat of the planet – see Figure 5. The rate of rise is not steady. The change in sea level in the 1990s was less than half the rate of rise in the most recent decade.
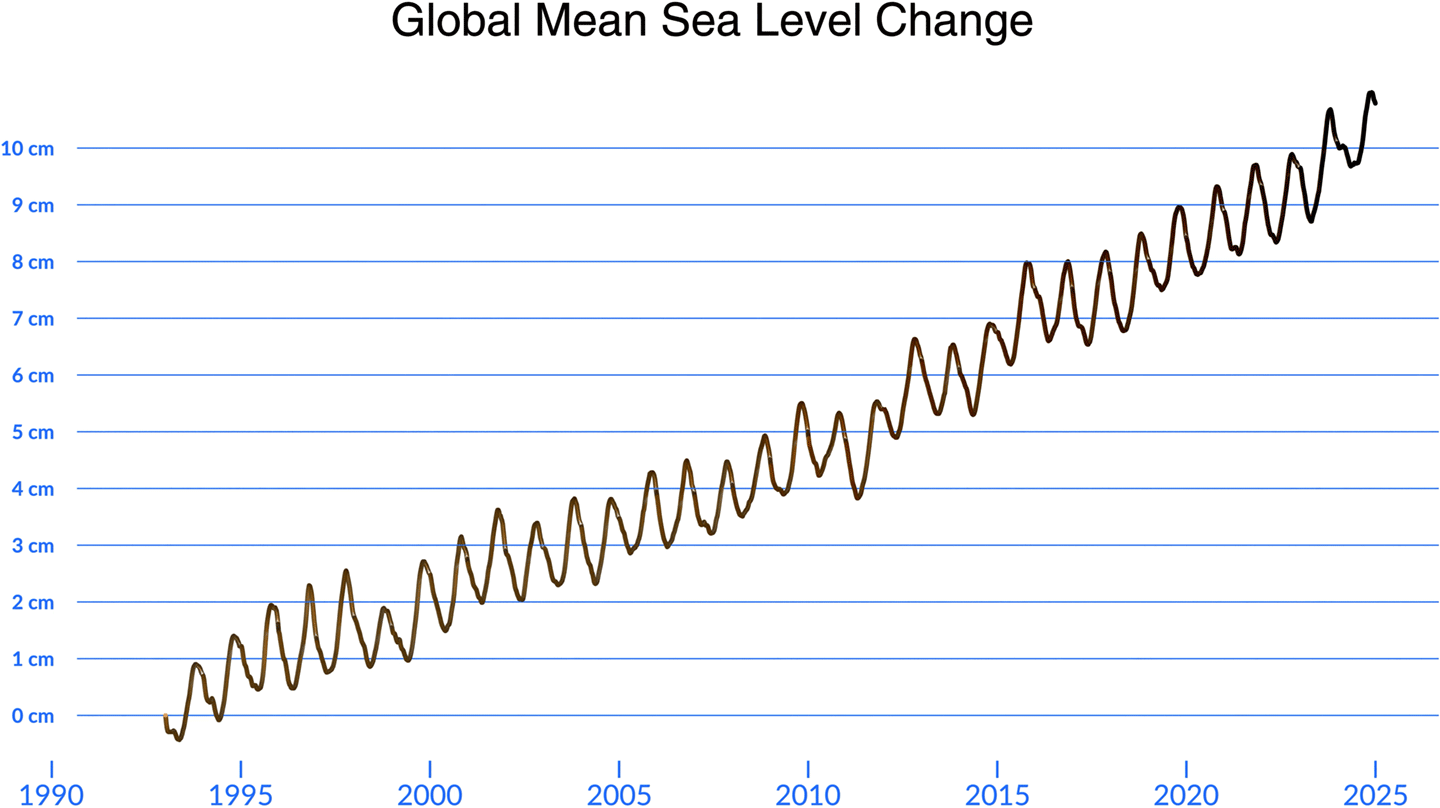 Figure 5. Sentinel-6B will continue to monitor the rise of the oceans. This record is composed of data from several different satellite altimetry missions dating back to TOPEX/Poseidon in 1992. Figure credit: NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio Conclusion
Figure 5. Sentinel-6B will continue to monitor the rise of the oceans. This record is composed of data from several different satellite altimetry missions dating back to TOPEX/Poseidon in 1992. Figure credit: NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio Conclusion
This unbroken record of sea level change stands as a crowning achievement to the accuracy, stability, and consistency of a series of satellite missions across more than three decades. This approach remains one of the most successful international collaborations to study our ever-changing Earth from space, and the launch of Sentinel-6B will stretch the record to nearly 40 years. With a vibrant international community of several hundred scientists and expert users, the discoveries made, and the value created by these observations will no doubt extend through 2030 and beyond. Although Sentinel-6B is nearly identical to its predecessor, a broad community of scientists, forecasters, operational users, and policymakers anxiously await its observations and the discoveries and utility they will bring through the remainder of this decade.
Joshua Willis
NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory
joshua.k.willis@jpl.nasa.gov
Severine Fournier
NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory
severine.fournier@jpl.nasa.gov
Details Last Updated Dec 22, 2025 Related Terms Earth Science


