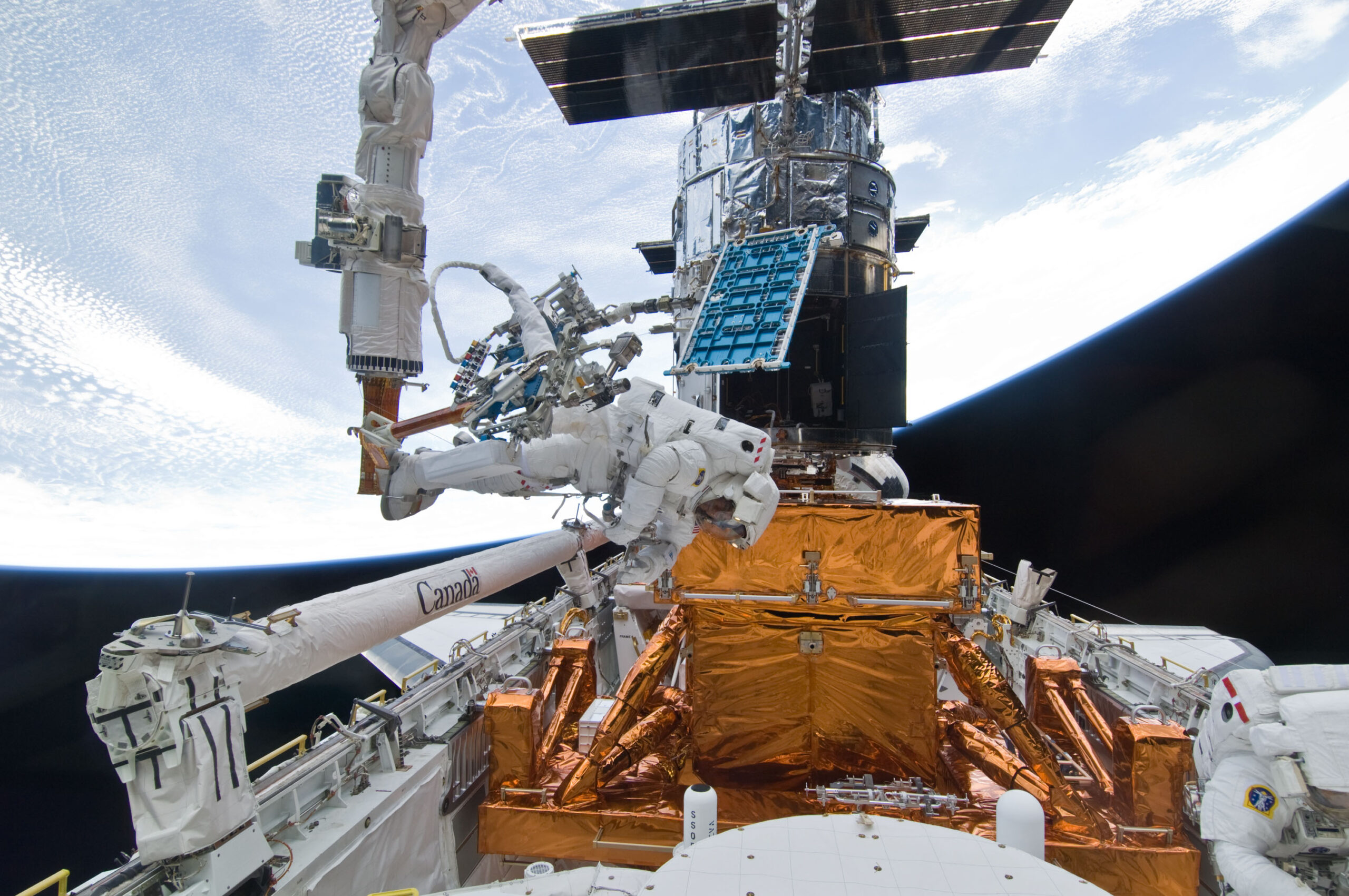
8 Min Read Hubble Celebrates the 15th Anniversary of Servicing Mission 4  Michael Good (on the end of the shuttle’s Remote Manipulator System) works to refurbish and upgrade Hubble during Servicing Mission 4. Credits:
Michael Good (on the end of the shuttle’s Remote Manipulator System) works to refurbish and upgrade Hubble during Servicing Mission 4. Credits:
NASA Fifteen years ago, human hands touched NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope for the last time.
As astronauts performed finishing tasks on the telescope during its final servicing mission in May 2009, they knew they had successfully concluded one of the most challenging and ambitious series of spacewalks ever conducted. But they couldn’t have known at the time what an impact they had truly made.
I had high hopes that Hubble would last at least five years more, and maybe even a little more to overlap with Webb. Here we are at 15 years and Hubble is going strong. The science from Hubble has been phenomenal.  John Grunsfeld
John Grunsfeld
NASA Astronaut
“I had high hopes that Hubble would last at least five years more, and maybe even a little more to overlap with Webb,” said astronaut and former associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate John Grunsfeld, who participated in three Hubble servicing missions and was lead mission specialist on SM4. “Here we are at 15 years and Hubble is going strong. The science from Hubble has been phenomenal.”
Today, more than three decades after its launch in 1990, Hubble continues to send stunning images back to Earth and conduct groundbreaking science. Much of the credit for the last 15 years belongs to Servicing Mission 4 (SM4), the fifth mission to repair and upgrade the telescope.
A Momentous Mission Launched on May 11, 2009 and spanning 12 days, Servicing Mission 4 was unlike any that had gone before, with stakes higher than they had been since the first mission to repair the telescope’s flawed vision. It would be the last space shuttle mission to Hubble, with the retirement of the shuttle announced in 2004. In addition to installing two new instruments and replacing and upgrading key components, astronauts would make repairs never envisioned when the telescope was designed.
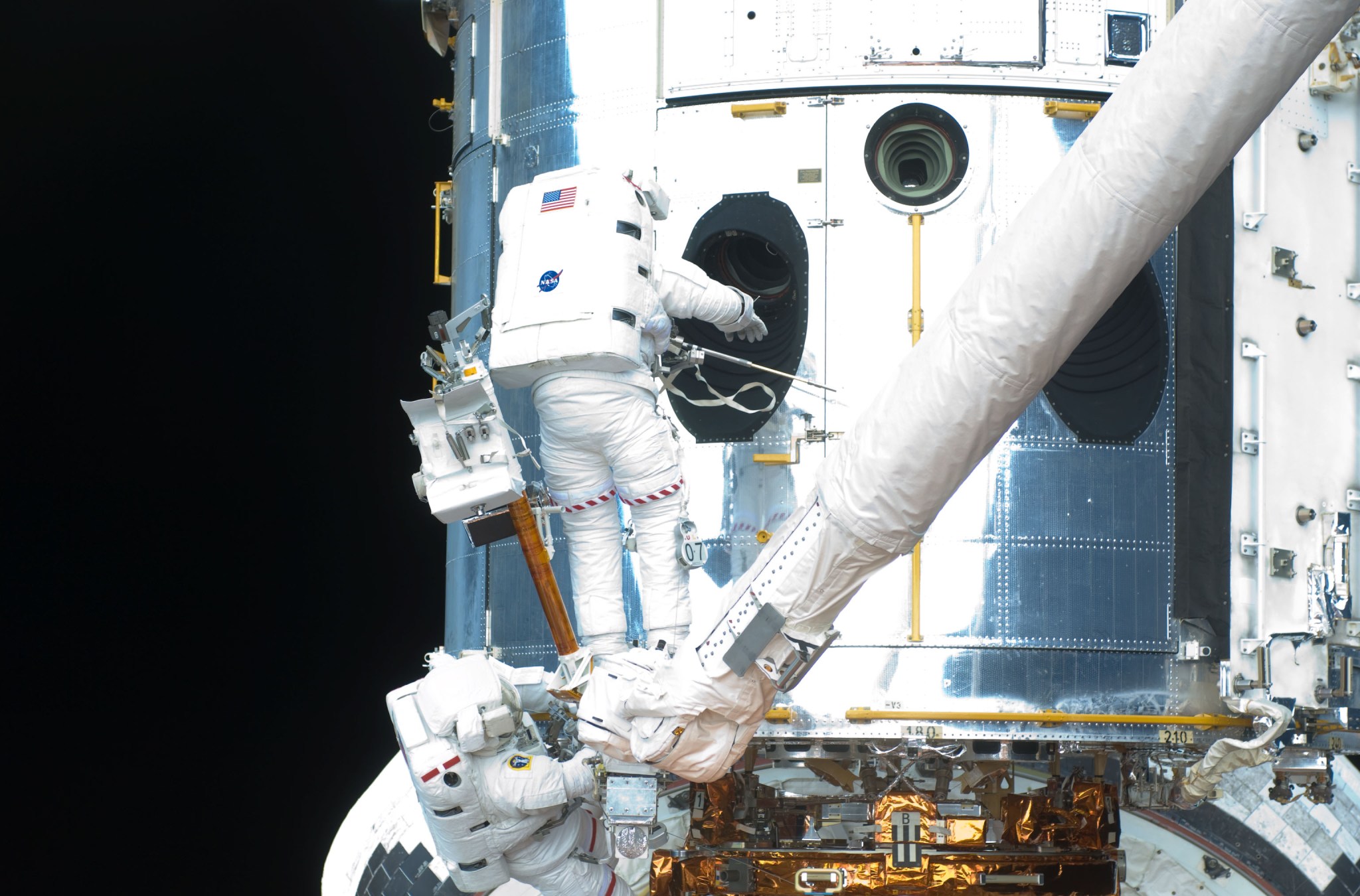 Astronauts Michael Good and Mike Massimino work to replace one of Hubble’s Rate Sensor Units, which contains two gyroscopes, during SM4. NASA For Megan McArthur, SM4 astronaut and primary operator of the shuttle’s robotic arm during the mission, the importance of the mission hit home before it even started, when the crew attended an event with people who worked on and with Hubble. Expecting a casual meet-and-greet to kick off the start of their Hubble training, they walked into an auditorium packed with people, who gave the astronauts a wild standing ovation.
Astronauts Michael Good and Mike Massimino work to replace one of Hubble’s Rate Sensor Units, which contains two gyroscopes, during SM4. NASA For Megan McArthur, SM4 astronaut and primary operator of the shuttle’s robotic arm during the mission, the importance of the mission hit home before it even started, when the crew attended an event with people who worked on and with Hubble. Expecting a casual meet-and-greet to kick off the start of their Hubble training, they walked into an auditorium packed with people, who gave the astronauts a wild standing ovation.
“We hadn’t done a single thing yet other than show up,” she recalled. “And I looked at one of my crewmates and we both teared up in that moment because it was such a powerful reminder of how important this was, and how meaningful it was for this huge community of engineers and scientists around the world who use that telescope to unlock the mysteries of the universe.”
…it was such a powerful reminder of how important this was, and how meaningful it was for this huge community of engineers and scientists around the world who use that telescope to unlock the mysteries of the universe.  Megan McArthur
Megan McArthur
NASA Astronaut
As the crew of seven astronauts headed toward Hubble on the space shuttle Atlantis, a second shuttle, Endeavour, waited on the launchpad in case a rescue was needed. After the loss of the space shuttle Columbia in 2003, Servicing Mission 4 was canceled due to safety concerns. Public support for the mission surged, and two years later it was reinstated and scheduled for 2008, only to be delayed for another year after the telescope’s critical Science Instrument Command and Data Handler suffered a failure. With the added time, engineers were able to add a replacement to the mission. By the time the SM4 launched, two instruments ― the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) and the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) ― had also experienced failures.
Hubble was designed and built for servicing in space, with modular, plug-and-play style components that could be easily swapped out. Astronauts had visited it four previous times leading up to SM4. (Servicing Mission 3 was split into two missions (3A and 3B) to get urgent repairs to Hubble quickly.) But during SM4, for the first time, astronauts cracked into two of the instruments to perform surgery in orbit. Using tools specially designed for the task, they opened up the ACS and STIS, swapped out components, rerouted power, and restored the instruments to their full capabilities.
The repairs were so effective that the two instruments have now gone more than twice as long without needing servicing than they achieved in the years prior to Servicing Mission 4.
Astronauts removed two older scientific instruments and added Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3), a powerful camera that sees some ultraviolet and infrared wavelengths as well as visible light, and the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS), which breaks ultraviolet light from cosmic objects into its component colors for analysis.
As this was certain to be the final shuttle mission to Hubble, the telescope had to be left in prime condition. Among other tasks, astronauts installed a new science computer and insulation. They replaced the telescope’s 19-year-old batteries and all of its gyroscopes, which determine how fast Hubble is turning and in what direction, with improved versions. Three of those gyroscopes have now operated longer than any gyroscopes previously installed on Hubble, and one has now been running continuously for 15 years, completing over 9 trillion revolutions.
The work could be challenging and intense. At one point, a bolt locking the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 into place wouldn’t turn. At another, a stripped screw on one of Hubble’s handrails blocked access to STIS and brought work to a standstill for hours, finally forcing astronaut Michael Massimino to physically wrench the handrail free.
“On each of my three trips to Hubble, the difficulty and scope of the work increased from mission to mission,” Grunsfeld said. “When we completed the final spacewalk on HST-SM4 in 2009, I was on top of the world ― figuratively, as we were in orbit around the Earth ― that we’d met and exceeded all expectations. The hard work and talent of the whole team is why we have an operating and productive observatory today.”
When the astronauts bid Hubble farewell, they left behind a telescope operating at peak performance ― and one that would energize humanity’s quest to understand the universe.
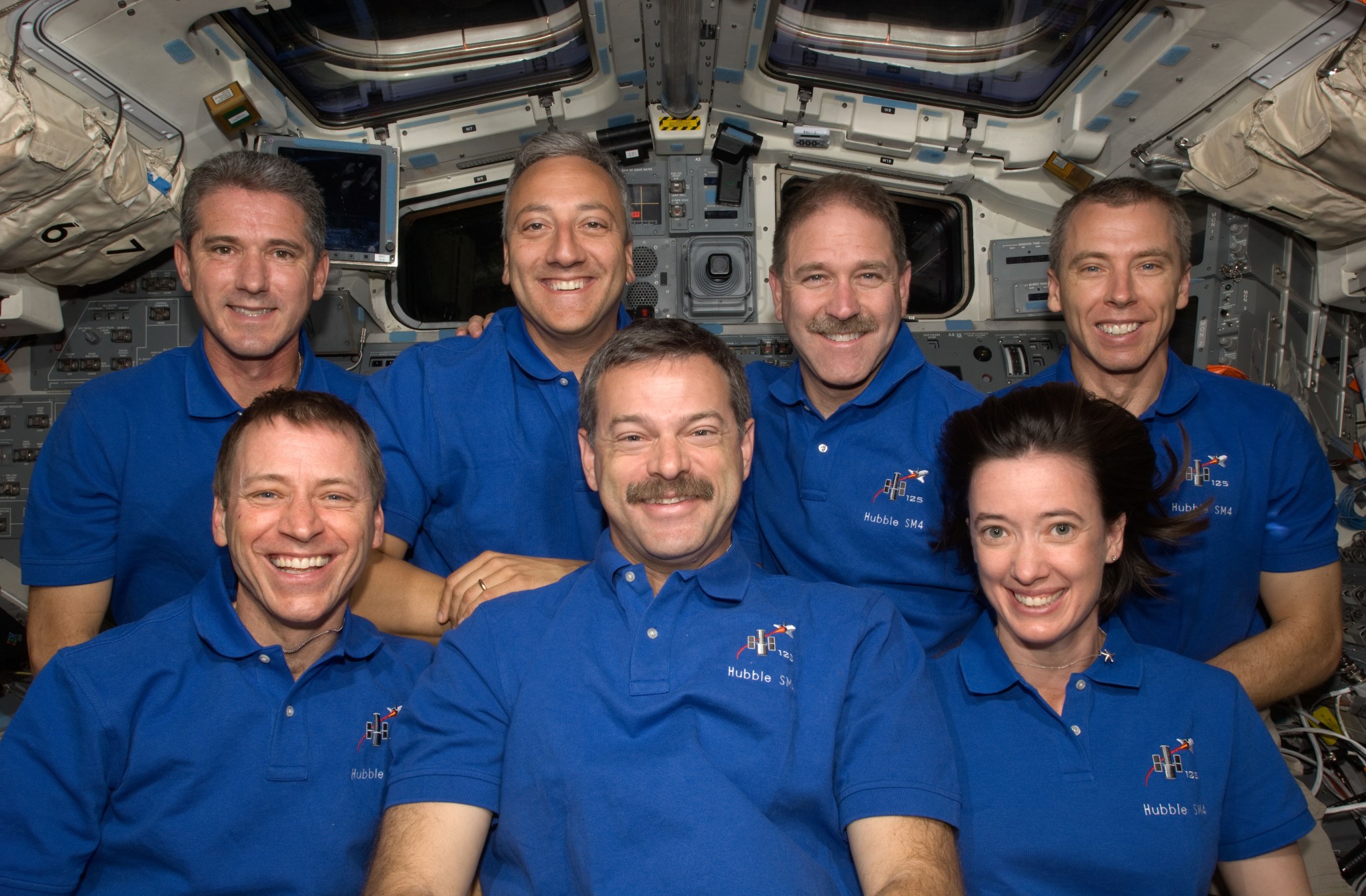 The Servicing Mission 4 crew pose for a photograph aboard the space shuttle Atlantis. Pictured in the front row (left to right) are astronauts Gregory C. Johnson, pilot; Scott Altman, commander; and Megan McArthur, mission specialist. Pictured in the back row (left to right) are astronauts Michael Good, Mike Massimino, John Grunsfeld, and Andrew Feustel, all mission specialists. NASA The resurrection of STIS and ACS and installation of WFC3 and COS provided by Servicing Mission 4 turned Hubble into a powerhouse that surpassed its previous capabilities. Since Hubble’s launch, its data have been the source of over 21,000 scientific papers. Over 6,000 of those ― around 30 percent ― arose from the new instruments installed on SM4 alone.
The Servicing Mission 4 crew pose for a photograph aboard the space shuttle Atlantis. Pictured in the front row (left to right) are astronauts Gregory C. Johnson, pilot; Scott Altman, commander; and Megan McArthur, mission specialist. Pictured in the back row (left to right) are astronauts Michael Good, Mike Massimino, John Grunsfeld, and Andrew Feustel, all mission specialists. NASA The resurrection of STIS and ACS and installation of WFC3 and COS provided by Servicing Mission 4 turned Hubble into a powerhouse that surpassed its previous capabilities. Since Hubble’s launch, its data have been the source of over 21,000 scientific papers. Over 6,000 of those ― around 30 percent ― arose from the new instruments installed on SM4 alone.
“There’s no doubt in my mind that the new and repaired instruments on Hubble are enabling scientific productivity like we’ve never seen before,” said Dr. Jennifer Wiseman, Hubble Space Telescope senior project scientist. “Being able to observe in wavelengths ranging from ultraviolet through the visible and into the near-infrared gives us a toolbox that is enabling new science in powerful ways that we never fully had before. Research by the scientific community is thriving based on Hubble data that have been taken since SM4.”
A Host of New Discoveries Since SM4, Hubble has charted its own path of discovery through the universe. It also works closely with other missions ― like the infrared-viewing James Webb Space Telescope ― to capture a complete picture of the cosmos.
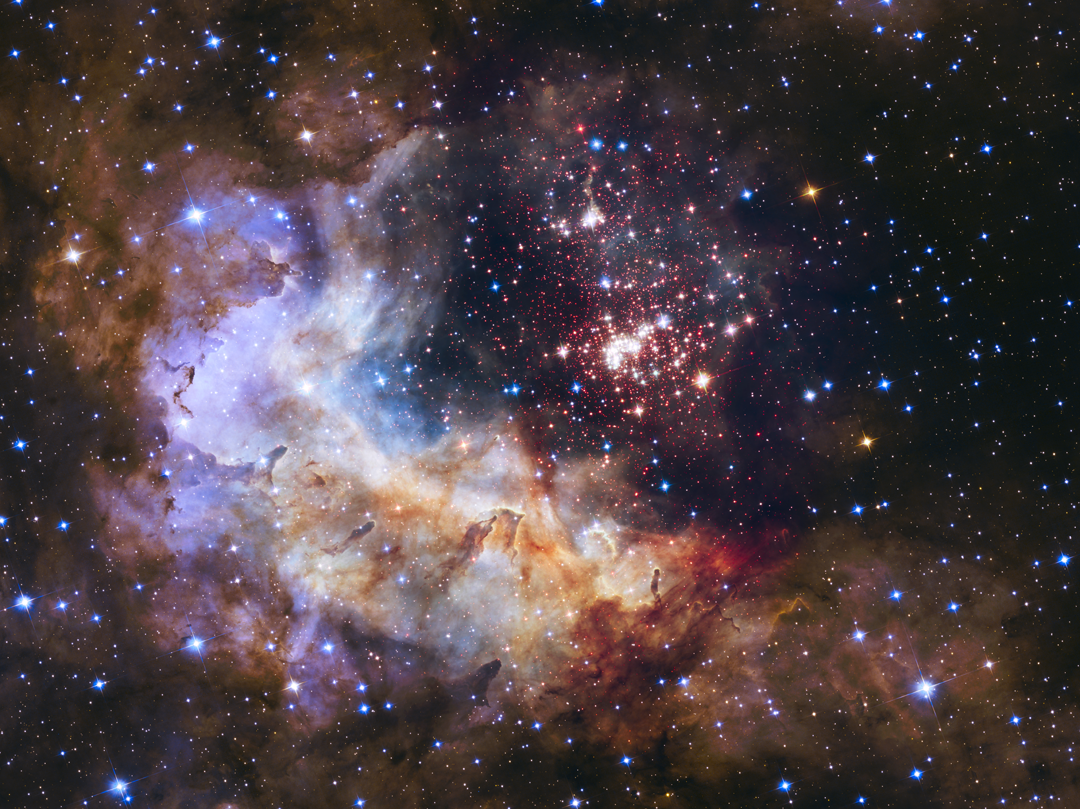 Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3, installed during Servicing Mission 4, captured this image of star cluster Westerlund 2, which contains some of the Milky Way galaxy’s hottest, brightest, and most massive stars. NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA), A. Nota (ESA/STScI) and the Westerlund 2 Science Team
Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3, installed during Servicing Mission 4, captured this image of star cluster Westerlund 2, which contains some of the Milky Way galaxy’s hottest, brightest, and most massive stars. NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA), A. Nota (ESA/STScI) and the Westerlund 2 Science Team  This image of NGC 5468, a galaxy located about 130 million light-years from Earth, combines data from the Hubble and James Webb space telescopes. This is the farthest galaxy in which Hubble has identified Cepheid variable stars. These are important milepost markers for measuring the expansion rate of the universe. The distance calculated from Cepheids has been cross-correlated with a type Ia supernova in the galaxy. Type Ia supernovae are so bright they are used to measure cosmic distances far beyond the range of the Cepheids, extending measurements of the universe’s expansion rate deeper into space.
This image of NGC 5468, a galaxy located about 130 million light-years from Earth, combines data from the Hubble and James Webb space telescopes. This is the farthest galaxy in which Hubble has identified Cepheid variable stars. These are important milepost markers for measuring the expansion rate of the universe. The distance calculated from Cepheids has been cross-correlated with a type Ia supernova in the galaxy. Type Ia supernovae are so bright they are used to measure cosmic distances far beyond the range of the Cepheids, extending measurements of the universe’s expansion rate deeper into space.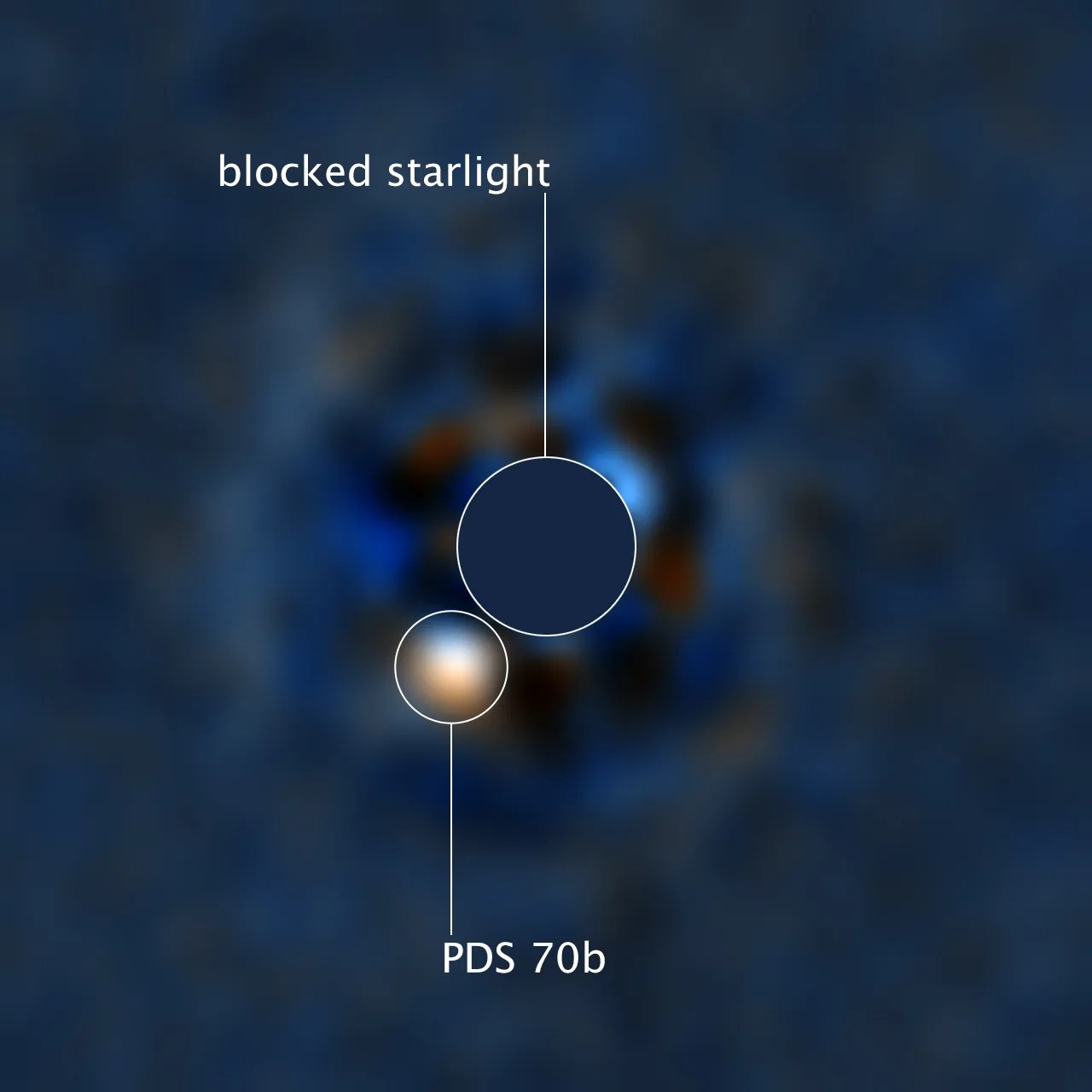  Hubble’s sensitivity to ultraviolet light revealed radiation from super-heated gas falling onto a world called PDS 70b. The glare of the star was blocked, allowing Hubble to directly observe PDS 70b accumulating mass. Located some 370 light-years from Earth, the planet is about five times the mass of Jupiter and growing at a snail’s pace. Researchers found that the planet is growing so slowly that if the rate remains steady for another million years, its bulk will increase by only about 1/100th of Jupiter’s mass
Hubble’s sensitivity to ultraviolet light revealed radiation from super-heated gas falling onto a world called PDS 70b. The glare of the star was blocked, allowing Hubble to directly observe PDS 70b accumulating mass. Located some 370 light-years from Earth, the planet is about five times the mass of Jupiter and growing at a snail’s pace. Researchers found that the planet is growing so slowly that if the rate remains steady for another million years, its bulk will increase by only about 1/100th of Jupiter’s mass  This Hubble image showcases the host galaxy of an exceptionally powerful fast radio burst, FRB 20220610A. Hubble’s sensitivity and sharpness allow it to observe the locations of these strange, fleeting, enormous blasts of energy ― including the farthest yet found. This compact group of multiple galaxies may be in the process of merging. They existed when the universe was only 5 billion years old.
This Hubble image showcases the host galaxy of an exceptionally powerful fast radio burst, FRB 20220610A. Hubble’s sensitivity and sharpness allow it to observe the locations of these strange, fleeting, enormous blasts of energy ― including the farthest yet found. This compact group of multiple galaxies may be in the process of merging. They existed when the universe was only 5 billion years old. 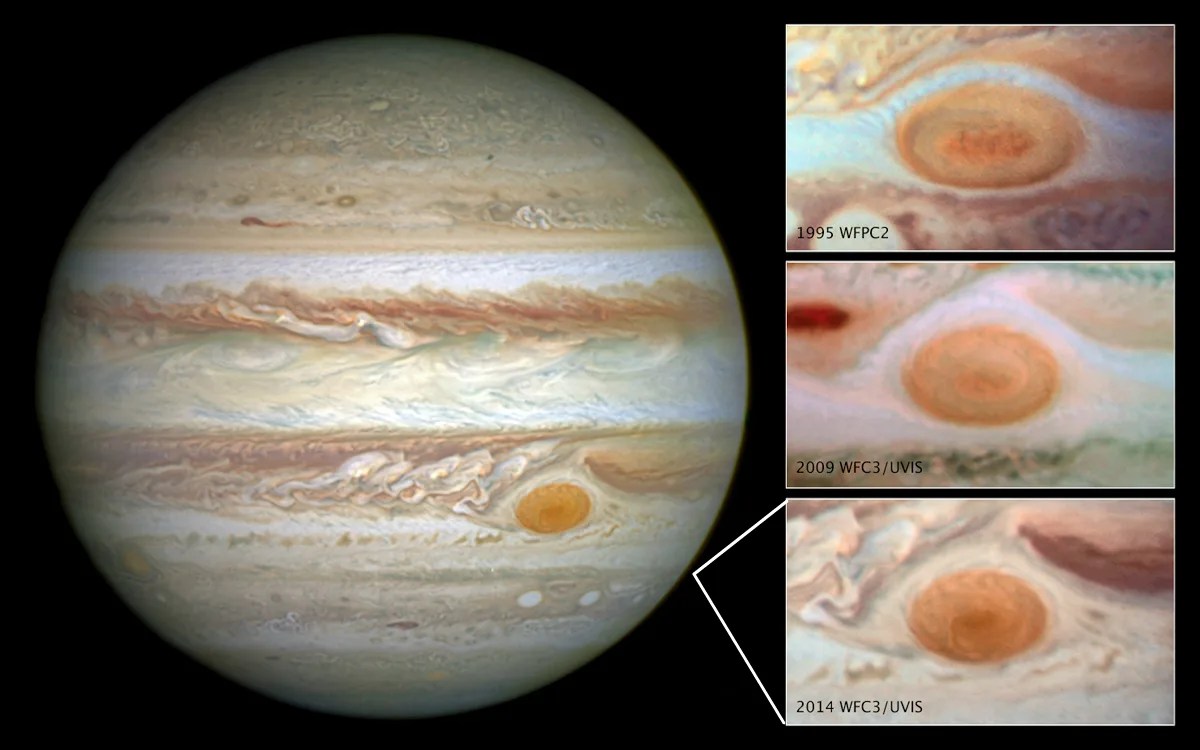 Hubble’s many years of observing Jupiter reveal that the planet’s trademark Great Red Spot is shrinking and its wind velocities are acceleration.
Hubble’s many years of observing Jupiter reveal that the planet’s trademark Great Red Spot is shrinking and its wind velocities are acceleration. 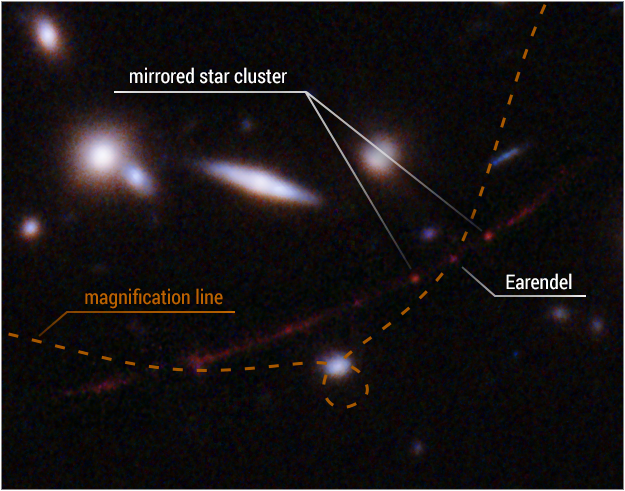 Hubble found the farthest individual star ever spotted, whose light has traveled 12.9 billion years to reach Earth. This detailed view highlights the star Earendel’s position along a ripple in space-time (dotted line) that magnifies it and makes it possible for the star to be detected over such a great distance. Also indicated is a cluster of stars that is mirrored on either side of the line of magnification. The distortion and magnification are created by the mass of a huge galaxy cluster located in between Hubble and Earendel. The mass of the galaxy cluster is so great that it warps the fabric of space, and looking through that region of space is like looking through a magnifying glass — along the edge of the glass or lens, the appearance of things on the other side are warped as well as magnified.
Hubble found the farthest individual star ever spotted, whose light has traveled 12.9 billion years to reach Earth. This detailed view highlights the star Earendel’s position along a ripple in space-time (dotted line) that magnifies it and makes it possible for the star to be detected over such a great distance. Also indicated is a cluster of stars that is mirrored on either side of the line of magnification. The distortion and magnification are created by the mass of a huge galaxy cluster located in between Hubble and Earendel. The mass of the galaxy cluster is so great that it warps the fabric of space, and looking through that region of space is like looking through a magnifying glass — along the edge of the glass or lens, the appearance of things on the other side are warped as well as magnified.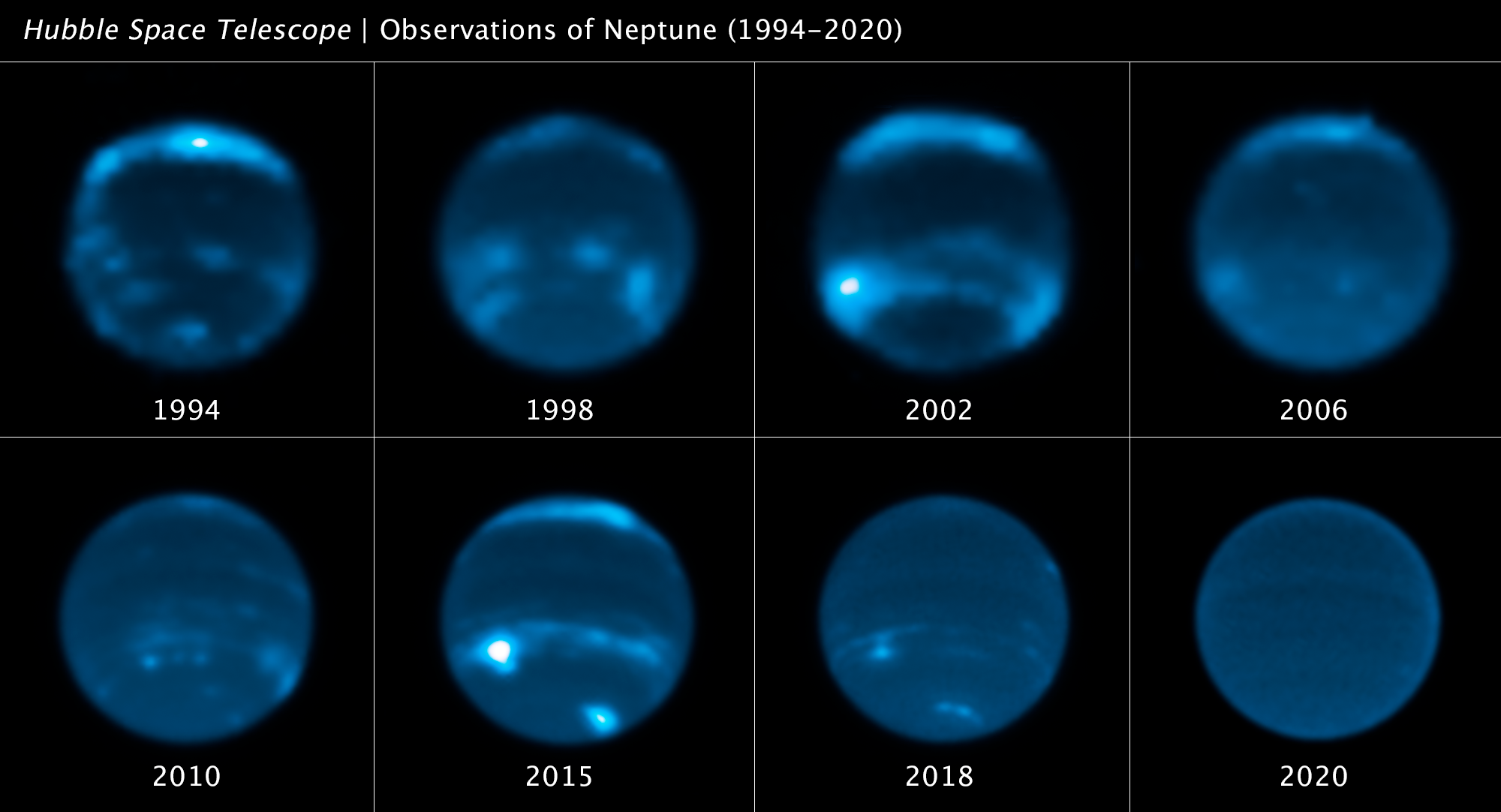  Hubble observations linked Neptune’s clouds to the solar cycle, showing that clouds increase every two years after the peak of an 11-year cycle, despite Neptune’s distance from the Sun.
Hubble observations linked Neptune’s clouds to the solar cycle, showing that clouds increase every two years after the peak of an 11-year cycle, despite Neptune’s distance from the Sun.  This Hubble image reveals a dense globular cluster called Messier 4. The cluster holds several hundred thousand stars and Hubble observations lead astronomers to suspect that an intermediate-mass black hole, weighing as much as 800 times the mass of our Sun, is lurking, unseen, at its core.
This Hubble image reveals a dense globular cluster called Messier 4. The cluster holds several hundred thousand stars and Hubble observations lead astronomers to suspect that an intermediate-mass black hole, weighing as much as 800 times the mass of our Sun, is lurking, unseen, at its core. 
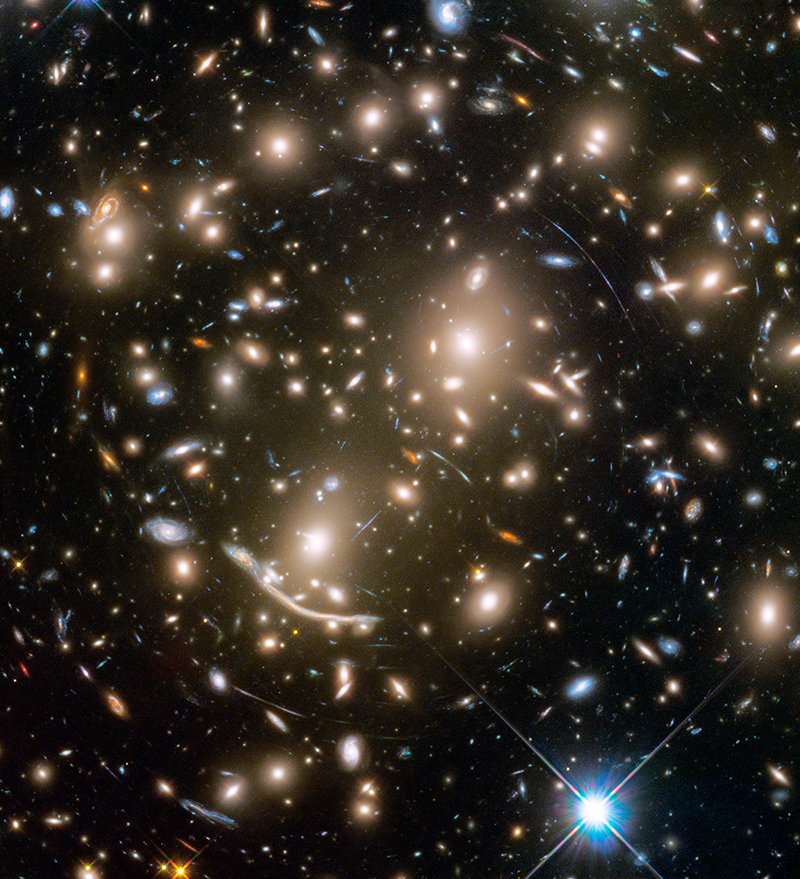 Hubble’s observations of galaxies have helped us better understand their origins and evolution. This Hubble image of galaxy cluster Abell 370, located approximately 4 billion light-years away, also reveals more distant galaxies that are behind the large cluster. They form curves and arcs as their light is magnified and warped by the powerful gravitational lens created by the galaxy cluster.
Hubble’s observations of galaxies have helped us better understand their origins and evolution. This Hubble image of galaxy cluster Abell 370, located approximately 4 billion light-years away, also reveals more distant galaxies that are behind the large cluster. They form curves and arcs as their light is magnified and warped by the powerful gravitational lens created by the galaxy cluster.
“Webb is really tuned to seeing the infrared wavelengths of light beyond what Hubble can pick up, but Webb cannot see the visible light and the ultraviolet light that Hubble can see, and we need all of those wavelengths of light for studying almost anything ― whether that’s planets, exoplanets, star systems, galaxies, the interstellar medium or cosmology,” Wiseman said. “So many proposals from scientists now involve both Hubble and Webb, because they are crucial partners for addressing some of the hottest topics in astrophysics.”
As Hubble starts its 35th year in orbit, the legacy of Servicing Mission 4 is on display in the telescope’s scientific bounty. “Hubble is more scientifically productive now than it’s ever been before, and it is playing a critical role in the portfolio of NASA’s flagship missions for science,” Wiseman said, noting that Hubble’s instruments have certain capabilities unmatched by anything else in orbit. “There are three big, strategic questions that NASA wants to address ― are we alone, how did we get here, and how does the universe work ― and Hubble is a primary facility for addressing them.”
Those scientific discoveries and the astounding images are the primary reason Hubble is celebrated around the globe, but its lasting presence in space is also a reminder of something even more profound.
McArthur recalled the moments after SM4 ended, when the crew had time to watch Hubble after it was released from the robotic arm. “There was nothing to do but gaze at it, and the feeling that I had at that point was a kind of awe or joy at the audacity of humans,” she said. “We have these amazing ideas like, let’s build a telescope and put it in orbit around the Earth to unlock the mysteries of the universe ― these very grand visions. And then here I am actually looking at it with my own eyes, this marvel of engineering that does exactly that. It gives me faith in humanity that when we put our minds to it, we can do just about anything, as long as we’re willing to work together.”
In May 2009, a brave team of astronauts embarked on a daring journey aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis. Their mission? To breathe new life into Hubble, ensuring its legacy of discovery could continue for years to come.
Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center; Lead Producer: Paul Morris Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
Explore More
Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble’s Impact on Human Spaceflight
Follow Hubble for the Latest News and Images Facebook logo @NASAHubble @NASAHubble Instagram logo @NASAHubble
Details Last Updated May 10, 2024 Editor Andrea Gianopoulos Location Goddard Space Flight Center Related Terms Astrophysics Astrophysics Division Goddard Space Flight Center Hubble Space Telescope Missions Science Mission Directorate
Keep Exploring Discover More Topics From NASA Hubble Space Telescope
Since its 1990 launch, the Hubble Space Telescope has changed our fundamental understanding of the universe.


Exploration is really the essence of the human spirit.

The NASA History Office serves two key functions: fulfilling the mandate of the 1958 “Space Act” calling for NASA to…



