Earth (ESD) Earth Explore Explore Earth Home Agriculture Air Quality Climate Change Freshwater Life on Earth Severe Storms Snow and Ice The Global Ocean Science at Work Earth Science at Work Technology and Innovation Powering Business Multimedia Image Collections Videos Data For Researchers About Us
before after
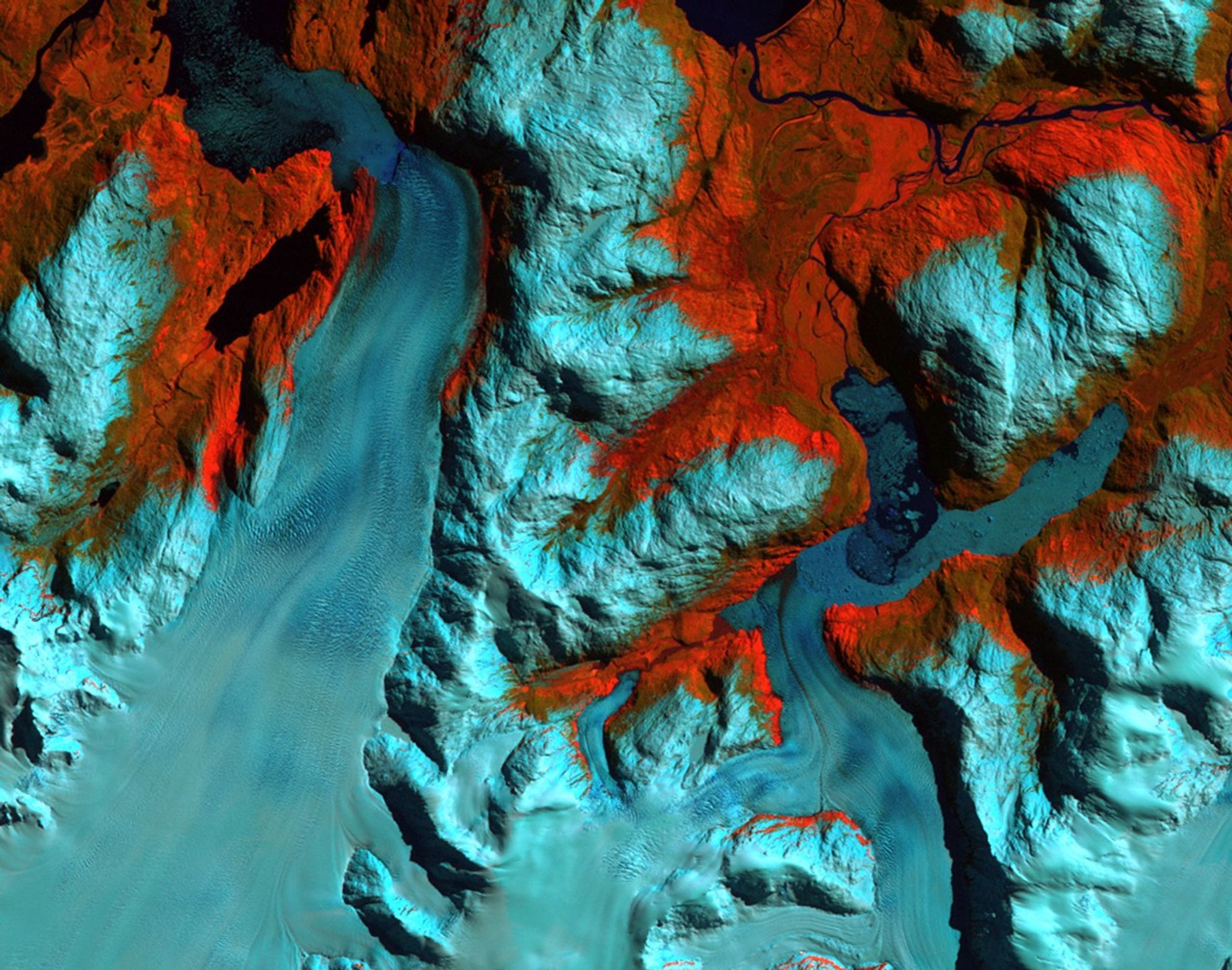 Patagonia, Chile. Left: September 18, 1986. Right: August 5, 2002. The 1986 image shows the region prior to a major retreat of the glaciers. The 2002 image shows a retreat of nearly 10 kilometers (6.2 miles) of the glacier on the left side. The smaller glacier on the right has receded more than 2 kilometers (1.2 miles). In front of the smaller glacier, two ribbon lakes have formed behind the debris left by the glacier’s advance. Scientists and government managers are using satellite imagery like this to monitor the retreat of the glaciers and the impact on water bodies caused by the changes in the glaciers’ size and direction. Left image taken by the Thematic Mapper sensor onboard Landsat 5. Right image taken by the Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus sensor onboard Landsat 7. Source: USGS Landsat Missions Gallery, “Patagonia Region – Retreating Glaciers,” U.S. Department of the Interior / U.S. Geological Survey. NASA/USGS
Patagonia, Chile. Left: September 18, 1986. Right: August 5, 2002. The 1986 image shows the region prior to a major retreat of the glaciers. The 2002 image shows a retreat of nearly 10 kilometers (6.2 miles) of the glacier on the left side. The smaller glacier on the right has receded more than 2 kilometers (1.2 miles). In front of the smaller glacier, two ribbon lakes have formed behind the debris left by the glacier’s advance. Scientists and government managers are using satellite imagery like this to monitor the retreat of the glaciers and the impact on water bodies caused by the changes in the glaciers’ size and direction. Left image taken by the Thematic Mapper sensor onboard Landsat 5. Right image taken by the Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus sensor onboard Landsat 7. Source: USGS Landsat Missions Gallery, “Patagonia Region – Retreating Glaciers,” U.S. Department of the Interior / U.S. Geological Survey. NASA/USGS
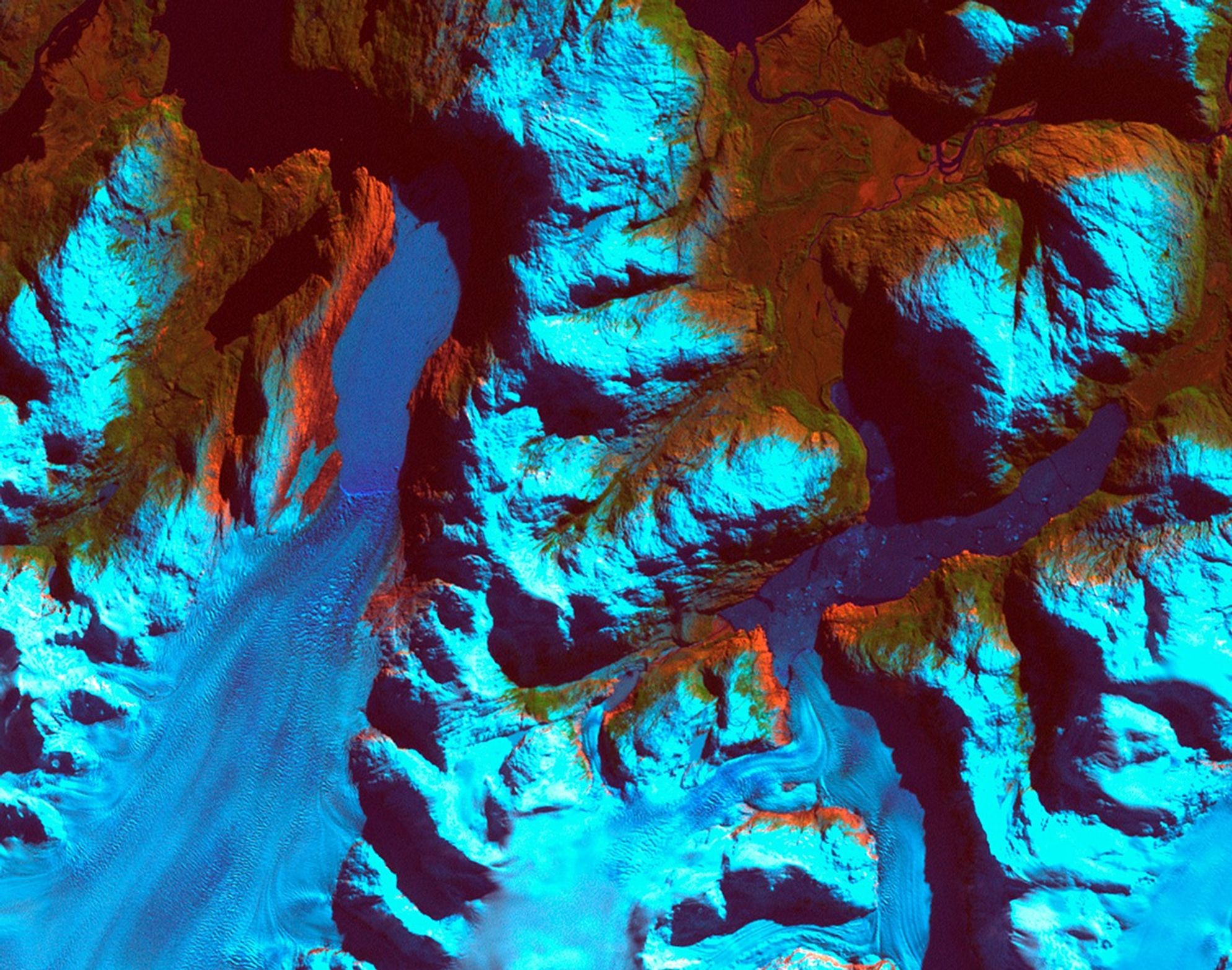 Patagonia, Chile. Left: September 18, 1986. Right: August 5, 2002. The 1986 image shows the region prior to a major retreat of the glaciers. The 2002 image shows a retreat of nearly 10 kilometers (6.2 miles) of the glacier on the left side. The smaller glacier on the right has receded more than 2 kilometers (1.2 miles). In front of the smaller glacier, two ribbon lakes have formed behind the debris left by the glacier’s advance. Scientists and government managers are using satellite imagery like this to monitor the retreat of the glaciers and the impact on water bodies caused by the changes in the glaciers’ size and direction. Left image taken by the Thematic Mapper sensor onboard Landsat 5. Right image taken by the Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus sensor onboard Landsat 7. Source: USGS Landsat Missions Gallery, “Patagonia Region – Retreating Glaciers,” U.S. Department of the Interior / U.S. Geological Survey. NASA/USGS beforeafter
Patagonia, Chile. Left: September 18, 1986. Right: August 5, 2002. The 1986 image shows the region prior to a major retreat of the glaciers. The 2002 image shows a retreat of nearly 10 kilometers (6.2 miles) of the glacier on the left side. The smaller glacier on the right has receded more than 2 kilometers (1.2 miles). In front of the smaller glacier, two ribbon lakes have formed behind the debris left by the glacier’s advance. Scientists and government managers are using satellite imagery like this to monitor the retreat of the glaciers and the impact on water bodies caused by the changes in the glaciers’ size and direction. Left image taken by the Thematic Mapper sensor onboard Landsat 5. Right image taken by the Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus sensor onboard Landsat 7. Source: USGS Landsat Missions Gallery, “Patagonia Region – Retreating Glaciers,” U.S. Department of the Interior / U.S. Geological Survey. NASA/USGS beforeafter
Before and After
Patagonia Glacier retreat, Chile September 18, 1986 – August 5, 2002
CurtainToggle
Image Details
Patagonia, Chile. Left: September 18, 1986. Right: August 5, 2002. The 1986 image shows the region prior to a major retreat of the glaciers. The 2002 image shows a retreat of nearly 10 kilometers (6.2 miles) of the glacier on the left side. The smaller glacier on the right has receded more than 2 kilometers (1.2 miles). In front of the smaller glacier, two ribbon lakes have formed behind the debris left by the glacier’s advance. Scientists and government managers are using satellite imagery like this to monitor the retreat of the glaciers and the impact on water bodies caused by the changes in the glaciers’ size and direction. Left image taken by the Thematic Mapper sensor onboard Landsat 5. Right image taken by the Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus sensor onboard Landsat 7. Source: USGS Landsat Missions Gallery, “Patagonia Region – Retreating Glaciers,” U.S. Department of the Interior / U.S. Geological Survey.
Downloads Image 1
JPEG
(3 MB)
JPEG
(3 MB)
Keep Exploring Explore Earth Science

In order to study the Earth as a whole system and understand how it is changing, NASA develops and supports…

NASA Earth Science helps Americans respond to challenges and societal needs — such as wildland fires, hurricanes, and water supplies…





