Curiosity NavigationCuriosityMission OverviewWhere is Curiosity?Mission UpdatesScienceOverviewInstrumentsHighlightsExploration GoalsNews and FeaturesMultimediaCuriosity Raw ImagesMars ResourcesMars MissionsMars Sample ReturnMars Perseverance RoverMars Curiosity RoverMAVENMars Reconnaissance OrbiterMars OdysseyMore Mars MissionsAll PlanetsMercuryVenusEarthMarsJupiterSaturnUranusNeptunePluto & Dwarf Planets 2 min read
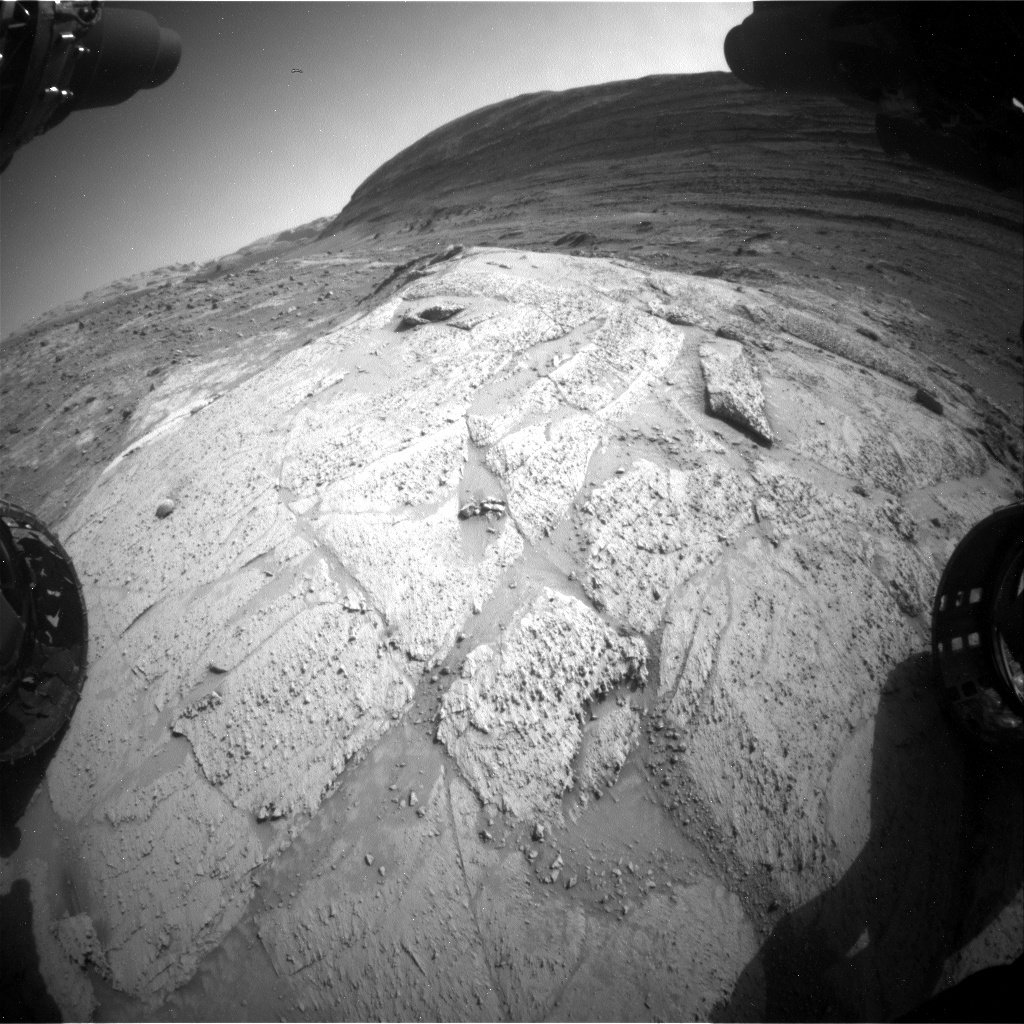
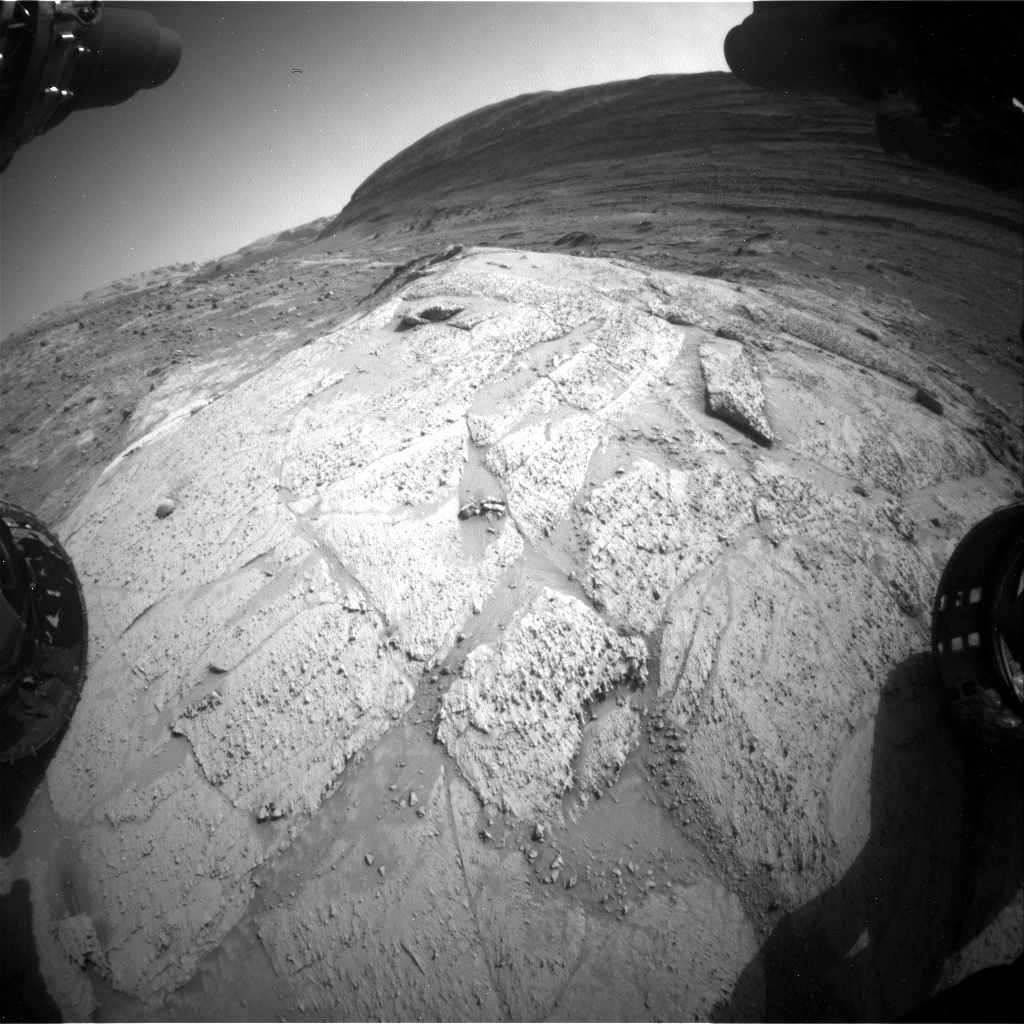
Sols 4248-4249: Lunch at Fairview Dome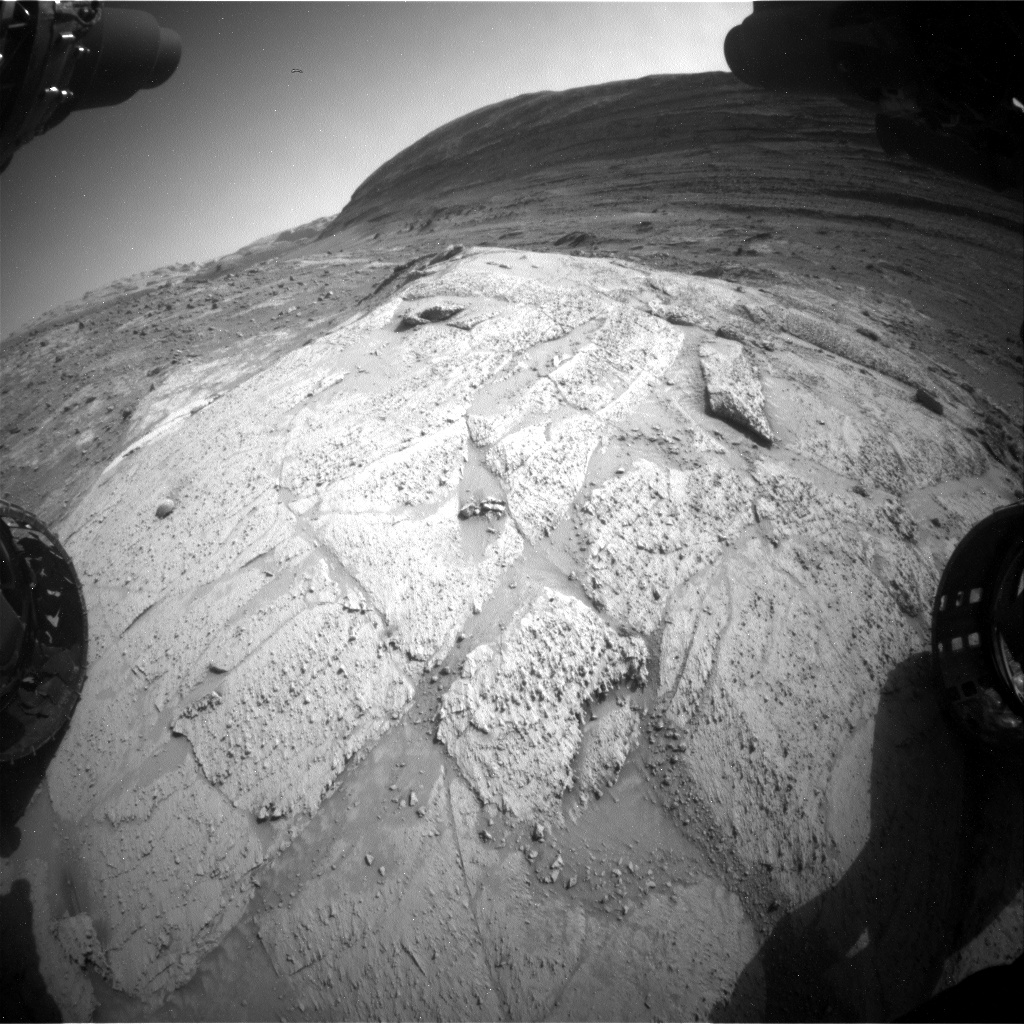  This image was taken by Front Hazard Avoidance Camera (Front Hazcam) onboard NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity on Sol 4246 – Martian day 4,246 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission – on July 16, 2024, at 23:32:19 UTC. Earth planning date: Wednesday, July 17, 2024
This image was taken by Front Hazard Avoidance Camera (Front Hazcam) onboard NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity on Sol 4246 – Martian day 4,246 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission – on July 16, 2024, at 23:32:19 UTC. Earth planning date: Wednesday, July 17, 2024
We started our day at an outcrop called “Fairview Dome,” a light-colored rock so big that it can easily be seen from orbit! We have had our eye on Fairview Dome since Curiosity descended into the Gediz Vallis channel. As a geologist who has spent a lot of time in the field, I imagined this as a perfect place to drop my backpack, enjoy my lunch, and soak in the stunning panoramic views from this vantage point mid-channel.
The science team opted to stay for two full days of contact science at Fairview Dome and assembled a plan consisting of numerous science observations. In the workspace directly in front of the rover’s wheels, we analyzed Fairview Dome using the dust removal tool, APXS, and MAHLI instruments at a target called “Amphitheater Dome.” The ChemCam team selected two LIBS targets on the Fairview Dome outcrop – “Columbia Finger” and “Agnew Meadows” – to analyze the chemistry. Mastcam planned four stereo mosaics on sol 4248 to image the rover’s surroundings, including the floor of upper Gediz Vallis, the floor of the upper Gediz Vallis ridge, the upper Gediz Vallis ridge channel, and a rock near the rover named “Tresidder Peak.” On the following sol, Mastcam assembled what will surely be a breathtaking, postcard-worthy, 360-degree mosaic of our current location.
Rounding out Curiosity’s to-do list for this two-sol plan, ChemCam took two long-distance RMI images to document the stratigraphy of the rocks looking up Gediz Vallis toward the south. Science team members in the environmental theme group planned observations including a suprahorizon movie to look at clouds, a dust devil movie, and a mastcam tau survey to measure the amount of dust in the Martian atmosphere.
Today, I served as the science team member responsible for compiling and organizing the details for each activity from the geology and mineralogy theme groups. Despite the intensity of the planning session, the spectacular views at Fairview Dome made me pause to appreciate where we are and how far Curiosity has come. And with so much striking geology still in front of us, it is indeed a very exciting time to be exploring on Mars!
Written by Sharon Wilson Purdy, Planetary Geologist at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum
Keep Exploring Discover More Topics From NASA Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun, and the seventh largest. It’s the only planet we know of inhabited…



 2 min read Sols 4246-4247: Next Stop: Fairview Dome Article 2 days ago
2 min read Sols 4246-4247: Next Stop: Fairview Dome Article 2 days ago  3 min read Sols 4243-4245: Exploring Stubblefield Canyon Article 2 days ago
3 min read Sols 4243-4245: Exploring Stubblefield Canyon Article 2 days ago  2 min read Sols 4241–4242: We Can’t Go Around It…We’ve Got To Go Through It! Article 6 days ago
2 min read Sols 4241–4242: We Can’t Go Around It…We’ve Got To Go Through It! Article 6 days ago